Subfamily: Deltarhabdovirinae
Genus: Gammahymrhavirus
Distinguishing features
Viruses assigned to the genus Gammahymrhavirus form a distinct monophyletic group based on well-supported Maximum Likelihood or Maximum Clade Credibility trees inferred from complete L sequences. Members of the genus have been detected in hymenopteran insects (Hymenoptera) including bees and wasps. They are distinct phylogenetically from viruses assigned to the genera Alphahymrhavirus and Betahymrhavirus.
Virion
Morphology
Virion morphology is unknown.
Nucleic acid
The genomes consist of a single molecule of negative-sense, single-stranded RNA of approximately 13.4–13.5 kb (Li et al., 2023).
Proteins
The N, P, M, G and L proteins share sequence homology and/or structural characteristics with the cognate proteins of other rhabdoviruses.
Genome organisation and replication
The genomes include the five canonical rhabdovirus structural protein genes (N, P, M, G and L) and at least one additional gene between the M and G genes (Figure 1 Gammahymrhavirus).
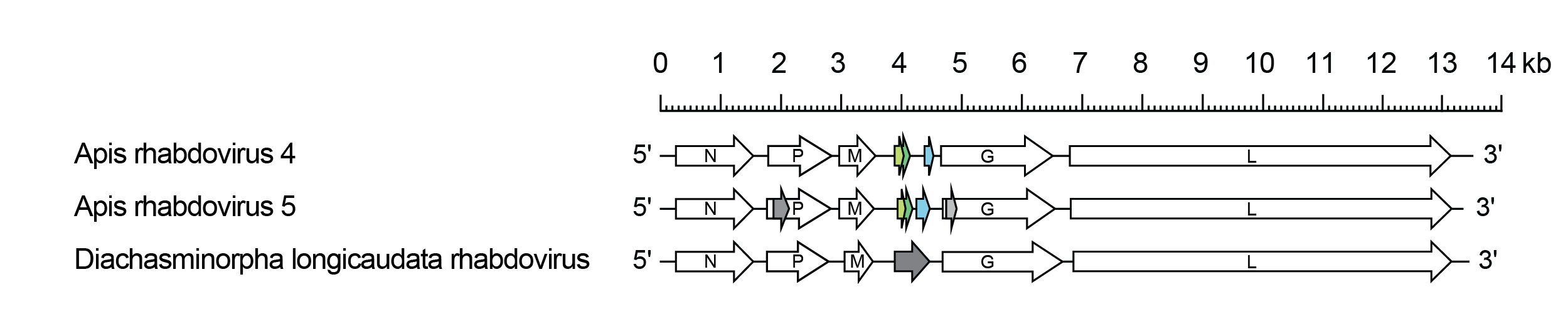 |
| Figure 1 Gammahymrhavirus. Schematic representation of gammahymrhavirus genomes shown in reverse (positive-sense) polarity. The genomes contain long open reading frames (ORFs) in the N, P, M, G and L genes (open arrows) along with at least one additional gene between the M and G genes which may encode overlapping ORFs. Alternative ORFs in the P and G genes of Apis rhabdovirus 5 (grey) may or may not be expressed. Those small ORFs encoding homologous proteins are shown in the same colour (lime, forest green or blue). |
Biology
The viruses assigned to this genus were discovered by metagenomic sequencing of bees or endoparasitoid wasps. Apis rhabdovirus 4 (species Gammahymrhavirus mellifera) was detected in Asian honey bees (Apis mellifera) collected in Zhejiang Province, China (Li et al., 2023). Apis rhabdovirus 5 (species Gammahymrhavirus cerana) was detected in European honey bees (Apis cerana) collected in Heilongjiang Province, China (Li et al., 2023). Diachasminorpha longicaudata rhabdovirus (species Gammahymrhavirus longicaudata) was detected in endoparasitoid wasps (Diachasminorpha longicaudata) of tephritid fruit flies collected in Florida, USA. No isolates of the viruses have yet been reported.
Species demarcation criteria
Viruses assigned to different species within the genus have several of the following characteristics: A) minimum amino acid sequence divergence of 10% in the N proteins; B) minimum amino acid sequence divergence of 10% in the L proteins; C) minimum amino acid sequence divergence of 15% in the G proteins; D) significant differences in genome organisation as evidenced by numbers and locations of ORFs; E) they can be distinguished in virus neutralisation tests; and F) they occupy different ecological niches as evidenced by differences in vertebrate hosts and or arthropod vectors.

