Subfamily: Alpharhabdovirinae
Genus: Thriprhavirus
Distinguishing features
Viruses assigned to the genus Thriprhavirus form a distinct monophyletic group based on well-supported Maximum Likelihood or Maximum Clade Credibility (MCC) trees inferred from complete L sequences. They have been detected in thrips (insects in the family Thripidae) and are most closely related to caligrhaviruses, which have been detected in sea lice.
Virion
Morphology
Viruses assigned to the genus have not yet been isolated or visualized by electron microscopy.
Nucleic acid
The genome consists of a single molecule of negative-sense, single-stranded RNA of approximately 12.8–13.2 kb.
Proteins
The N, P, M, G and L share sequence homology and/or structural characteristics with the cognate proteins of other rhabdoviruses. The small class 1a viroporin-like proteins encoded in the Gx ORF range from 121 to 124 amino acids (13.6 –14.0 kDa) and feature a very short N-terminal domain, a predicted hydrophobic transmembrane domain and a C-terminal domain that is rich in proline and basic residues.
Genome organisation and replication
Thriprhavirus genomes include five genes (N, P, M, G and L) encoding the structural proteins and an alternative ORF overlapping the start of the G gene that encodes a class 1a viroporin-like protein (Gx) (Figure 1 Thriprhavirus). The genomes also feature a very long 3′-untranslated region in the G gene which varies in length from 393–1,111 nt.
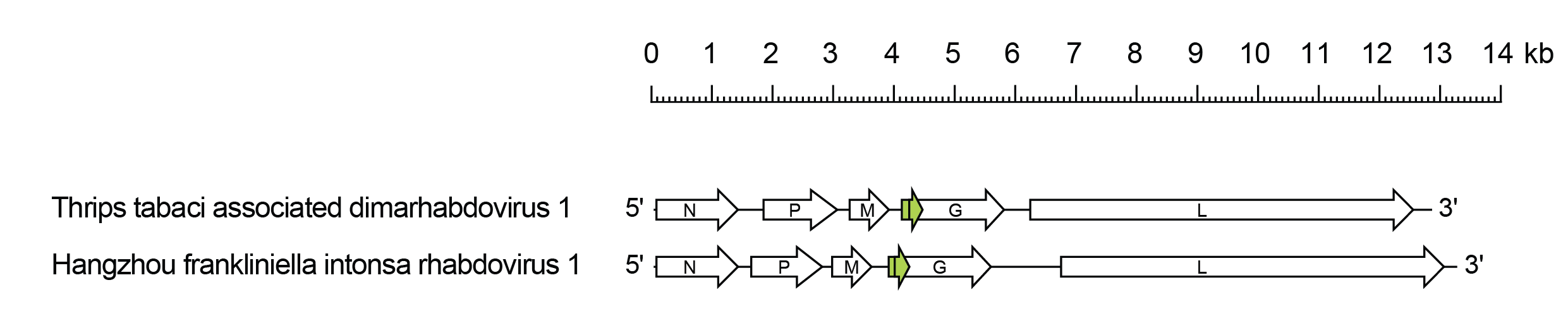 |
| Figure 1 Thriprhavirus. Schematic representation of thriprhavirus genomes shown in reverse (positive-sense) polarity. N, P, M, G and L represent ORFs encoding the structural proteins. The Gx ORFs (green) each encode a class 1a viroporin-like protein. |
Biology
Thriprhaviruses have been detected only by high-throughput sequencing of thrips. Thrips tabaci associated dimarhabdovirus 1 (species Thriprhavirus tabaci) was detected in onion thrips (Thrips tabaci) collected in Italy (Chiapello et al., 2021). Hangzhou Frankliniella intonsa rhabdovirus 1 (Thriprhavirus intonsa) was detected in European flower thrips (Frankliniella intonsa) collected in China.
Species demarcation criteria
Viruses assigned to different species within the genus Thriprhavirus have several of the following characteristics: A) minimum amino acid sequence divergence of 12% in the G protein; B) minimum amino acid sequence divergence of 8% in the L protein; C) minimum amino acid sequence divergence of 4% in the N protein; D) can be distinguished in virus neutralization tests; E) exhibit significant differences in genome organization as evidenced by numbers and locations of ORFs; and F) occupy different ecological niches as evidenced by differences in hosts and or arthropod vectors.
Related, unclassified viruses
| Virus name | Accession number | Virus abbreviation |
| Hubei dimarhabdovirus 4 | KX884435 | HbDRV4 |
Virus names and virus abbreviations are not official ICTV designations.

