Subfamily: Betarhabdovirinae
Genus: Cytorhabdovirus
Distinguishing features
Historically, two genera of unsegmented plant rhabdoviruses (Cytorhabdovirus and Nucleorhabdovirus) were established based on the sites of member virus replication and morphogenesis. Cytorhabdoviruses are unsegmented plant rhabdoviruses that replicate and mature in the cytoplasm of infected cells. They form a monophyletic group based on well-supported Maximum Likelihood or Maximum Clade Credibility trees inferred from complete L protein sequences. The genus classification based on monophyly has thus far correlated with classification by intracytoplasmic virus maturation.
Virion
Morphology
Enveloped virions are bacilliform, 60–75 nm in diameter and 200–350 nm long (Dietzgen 2002, Jackson et al., 2005a).
Physicochemical and physical properties
The buoyant density in sucrose or potassium tartrate is 1.19–1.20 g cm−3 (Dietzgen 2002). The lipid envelope is derived from the cytoplasmic membranes of plant or insect host cells (Jackson et al., 2005a).
Nucleic acid
The negative-sense, single-stranded RNA genome of 9.8–14.5 kb is unsegmented. Six to eleven mRNAs, one for each of the encoded proteins, have been identified in infected plants.
Proteins
N, P, M, G and L represent the five canonical rhabdovirus structural proteins. P of lettuce necrotic yellows virus (LNYV; species Cytorhabdovirus lactucanecante) and alfalfa dwarf virus (ADV; species Cytorhabdovirus medicagonis) have RNA silencing suppressor activity (Mann et al., 2015, Bejerman et al., 2016, Mann et al., 2016b). The P3 proteins of LNYV and ADV (encoded in the 4b gene) localize to plasmodesmata and trans-complement movement of heterologous viruses between plant cells (Mann et al., 2016a). Colocasia bobone disease-associated virus (CBDaV; species Cytorhabdovirus colocasiae), ADV, strawberry crinkle virus (SCV; species Cytorhabdovirus fragariarugosus), northern cereal mosaic virus (NCMV; species Cytorhabdovirus gramineae) and barley yellow striate mosaic virus (BYSMV; species Cytorhabdovirus hordei) encode small proteins that have the structural characteristics of class 1a viroporins, similar to those detected commonly in mammalian rhabdoviruses. The functions of other accessory proteins are mostly unknown, but it has been recently suggested that P6 of BYSMV acts as a virus effector to downregulate JA signaling and induce plant attractiveness to insects (Gao et al., 2022).
Lipids
The lipoprotein envelope is derived from the host plant or the insect vector (Jackson et al., 2005a). Lipid composition is unknown.
Carbohydrates
LNYV G is glycosylated with a complex network of oligosaccharides containing N-acetylchitobiose, N-linked to asparagine residues. The carbohydrate binds to concanavalin A and can be removed by endoglycosidase F (Dietzgen and Francki 1988).
Genome organisation and replication
The LNYV genome organisation (12.8 kb) is similar to that of Sonchus yellow net virus (SYNV, see genus Betanucleorhabdovirus). Preceded by a non-coding 84 nt leader sequence, the gene order is 3′-N-P-4b-M-G-L-5′ (Figure 1 Cytorhabdovirus). The N gene encodes the nucleoprotein (or nucleocapsid protein), and the P, M, G and L genes encode the phosphoprotein (polymerase cofactor), matrix protein, glycoprotein and RNA polymerase, respectively. The 4b gene encodes a cell-to-cell movement protein (P3). The intergenic regions contain highly conserved consensus sequences. The 5′-non-coding trailer sequence of 187 nt has extensive complementarity to the 3′-leader. The NCMV genome is 13.2 kb with a gene order similar to that of LNYV, except for the presence of three additional small genes of unknown function between the P and M genes, and an additional gene between the G and L genes that encodes a class 1a viroporin-like protein. The genome of BYSMV (12.7 kb) is similar to that of NCMV, except that one of the additional small ORF (P5) located in an alternative frame within the P4 gene and expressed by a leaky scanning mechanism. The genome organisations of lettuce yellow mottle virus (LYMoV; species Cytorhabdovirus lactucamaculante) (12.9 kb), CBDaV (12.2 kb), ADV (14.5 kb) and SCV (14.5 kb) are similar to that of LNYV, except for the presence in SCV and ADV of one additional gene between the G and L genes encoding a class 1a viroporin-like protein. Alternative ORFs within the P gene also occur in several cytorhabdoviruses but it is not known if they are expressed.
Cytorhabdoviruses replicate in the cytoplasm of infected cells in association with masses of thread-like structures (viroplasms) (Jackson et al., 2005a). Virions bud in association with the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and accumulate in ER-derived vesicles (Chambers et al., 1965, Wolanski and Chambers 1971). A nuclear phase has been suggested but not proven in the replication of some cytorhabdoviruses (e.g., LNYV) (Wolanski and Chambers 1971). Evidence of the nuclear involvement in the replication of others is lacking (e.g., BYSMV). Endogenous transcriptase activity is readily detectable in cytorhabdovirus preparations (Francki and Randles 1972).
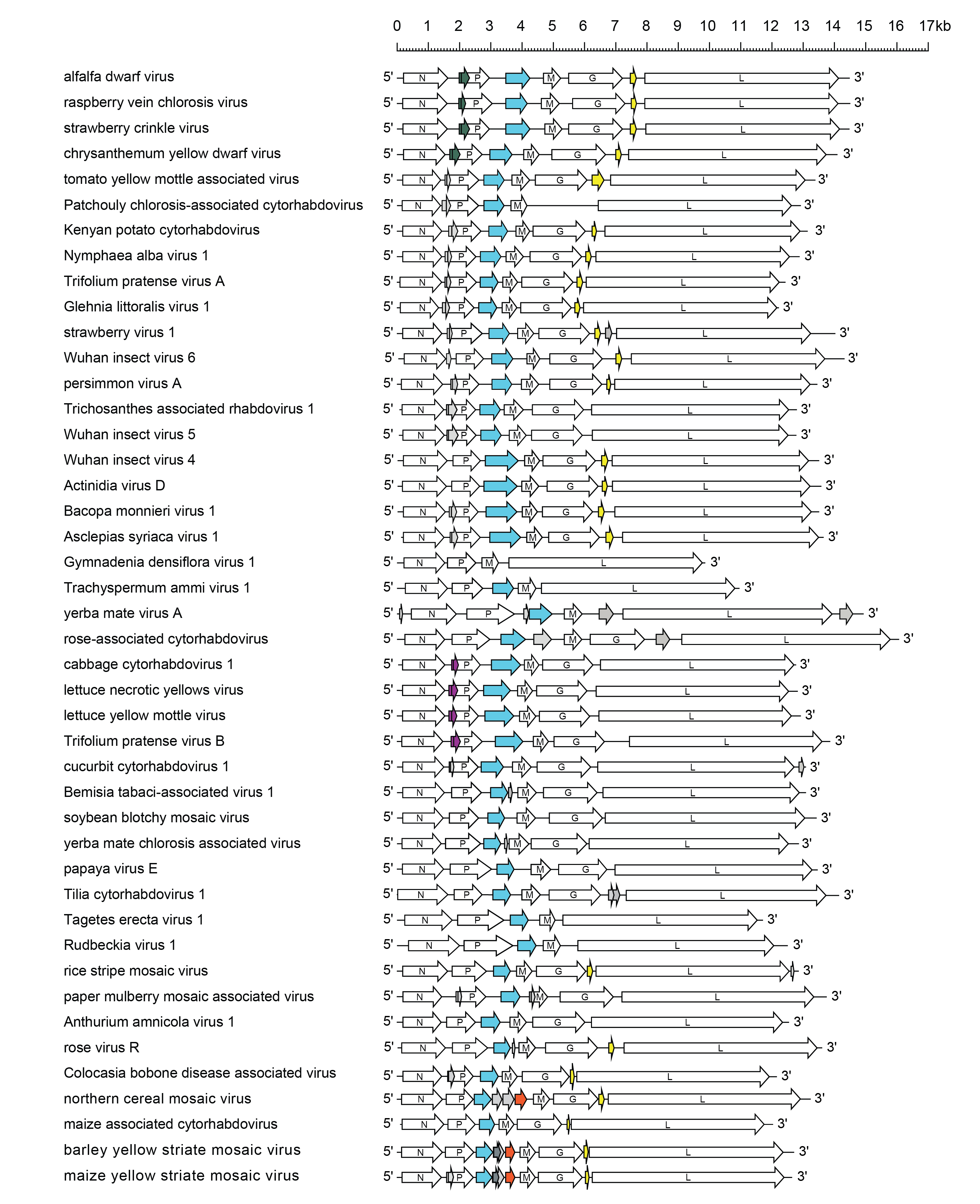 |
| Figure 1 Cytorhabdovirus. Schematic representation of a selection of cytorhabdovirus genomes shown in reverse (positive-sense) polarity. N, P, M, G and L represent ORFs encoding the structural proteins. ORFs encoding viral cell-to-cell movement proteins (blue) and predicted class 1a viroporin-like proteins (yellow) are shown. Other ORFs encode putative accessory proteins of unknown function, some of which occur as homologous sets (purple, dark green, dark grey or orange). ORFs with no obvious homologues are also shown (grey). In addition to those virus genomes shown: blackcurrant rhabdovirus 2 is similar to lettuce necrotic yellows virus; daphne virus 1 is similar to cabbage cytorhabdovirus 1; Hyptis latent virus is similar to chrysanthemum yellow dwarf virus; Pastinaca cytorhabdovirus 1 is similar to Trifolium pratense virus A; Sambucus virus 1 is similar to Wuhan insect virus 5; strawberry virus 2 is similar to lettuce yellow mottle virus; and Taraxacum cytorhabdovirus 1 is similar to Trifolium pratense virus B. |
Biology
A wide variety of monocot and dicot plants are susceptible to cytorhabdoviruses, although each virus usually has a restricted host range. Cytorhabdoviruses are transmitted by aphids (LNYV, ADV), planthoppers (NCMV, BYSMV), leafhoppers (rice stripe mosaic virus (RSMV; species Cytorhabdovirus oryzae) or whiteflies (papaya virus E [PpVE; species Cytorhabdovirus caricae]). Some viruses are also transmitted during vegetative propagation, and some can also be transmitted mechanically from infected sap. Seed transmission has not been reported, but was suggested to be involved in the transmission of Rudbeckia virus 1 (RudV1; species Cytorhabdovirus rudbeckiae) (Lee et al., 2022). In all carefully examined cases, viruses replicate in cells of the insect vector as well as in the plant host (Jackson et al., 2005a, Redinbaugh and Hogenhout 2005).
Species demarcation criteria
Viruses assigned to different species within the genus Cytorhabdovirus have several of the following characteristics: A) their complete genomes have nucleotide sequence identities of less than 75%; B) amino acid sequence identity in all cognate open reading frames is less than 80%; C) they occupy different ecological niches as evidenced by differences in hosts and/or arthropod vectors; and D) they can be clearly distinguished in serological tests or by nucleic acid hybridisation. Cytorhabdovirus species assignments are primarily determined by plant host range and vector specificity. Nucleic acid hybridisation and RT-PCR have been used to provide confirmation of species assignments and serological criteria have enabled verification of common viruses that infect different hosts. However, no cytorhabdovirus species have been defined unambiguously using serology. Hybridisation using cloned probes, RT-PCR and conserved L gene polymerase motif sequences has been used to differentiate viruses within the genus and to identify some strains.
Related, unclassified viruses
| Virus name | Accession number | Virus abbreviation |
| alfalfa cytorhabdovirus 1 | OK514706* | AlCRV1 |
| alfalfa cytorhabdovirus 2 | OK514707* | AlCRV2 |
| Arctium alphacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064262 | ArcACRV1 |
| Argyranthemum gammacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064345 | ArgGCRV1 |
| Aristolochia associated cytorhabdovirus | OR090884 | AaCV |
| Artemisia alphacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064263 | ArtACRV1 |
| Artemisia alphacytorhabdovirus 2 | BK064264 | ArtACRV2 |
| Artemisia alphacytorhabdovirus 3 | BK064265 | ArtACRV3 |
| Artemisia betacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064306 | ArtBCRV1 |
| Baccharis alphacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064266 | BacACRV1 |
| Begonia betacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064306 | BegBCRV1 |
| Betula betacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064307 | BetBCRV1 |
| Betula betacytorhabdovirus 2 | BK064308 | BetBCRV2 |
| Bouteloa betacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064309 | BouBCRV1 |
| Cardamine alphacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064267 | CarACRV1 |
| carrot gammacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064346 | CarGCRV1 |
| celery gammacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064347 | CelGCRV1 |
| Chelidonium yellow mottle associated virus | OR290114 | CheYMaV |
| Chrysanthemum alphacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064269 | ChrACRV1 |
| Chrysanthemum betacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064310 | ChrBCRV1 |
| Cnidium virus 2 | OQ442952 | CnV2 |
| Conopholis alphacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064270 | ConACRV1 |
| Coptis gammacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064348 | CopGCRV1 |
| coriander cytorhabdovirus 1 | OR536958 | CoCRV1 |
| Corylus betacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064311 | CorBCRV1 |
| Cucubita betacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064312 | CucBCRV1 |
| Cuscuta gammacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064349 | CusGCRV1 |
| Cuscuta gammacytorhabdovirus 2 | BK064350 | CusGCRV2 |
| Cynara alphacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064271 | CynACRV1 |
| Cypripedium betacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064313 | CypBCRV1 |
| Cypripedium gammacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064351 | CypGCRV1 |
| Dryobalanops betacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064314 | DryBCRV1 |
| Durio betacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064315 | DurBCRV1 |
| Epipactis gammacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064352 | EpiGCRV1 |
| Euphorbia alphacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064272 | EupACRV1 |
| Ficus alphacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064274 | FicACRV1 |
| Fraxinus gammacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064353 | FraGCRV1 |
| Fraxinus gammacytorhabdovirus 2 | BJ064354 | FraGCRV2 |
| garlic alphacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064275 | GarACRV1 |
| Geum alphacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064276 | GeuACRV1 |
| Gleditsia betacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064316 | GleBCRV1 |
| Glycyrrhiza betacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064317 | GlyBCRV1 |
| goji cytorhabdovirus A | OR489165 | GCVA |
| Hedera alphacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064277 | HedACRV1 |
| Helisoperma gammacytorhabdovirus 1 | BJ064355 | HelGCRV1 |
| Hepatica betacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064318 | HepBCRV1 |
| Hibiscus gammacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064356 | HibGCRV1 |
| Howea betacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064319 | HowBCRV1 |
| Ilex alphacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064278 | IleACRV1 |
| Ipomoea betacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064320 | IpoBCRV1 |
| Iranian citrus ringspot-associated virus | KP255976* | IrCRSaV |
| ivy vein banding virus | GQ249162*; GQ249163* | IVBV |
| Ixeris denticulata associated rhabdovirus | OQ927981 | IdaRV |
| Justicia betacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064321 | JusBCRV1 |
| Kobresia betacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064322 | KobBCRV1 |
| Leucadendron betacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064323 | LeuBCRV1 |
| Lonas gammacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064357 | LonGCRV1 |
| Lupinus gammacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064358 | LupGCRV1 |
| mango betacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064325 | ManBCRV1 |
| Medicago alphacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064279 | MedACRV1 |
| Mentha alphacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064280 | MenACRV1 |
| Morinda alphacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064281 | MorACRV1 |
| Morus betacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064326 | MorBCRV1 |
| Nitraria betacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064327 | NitBCRV1 |
| oak alphacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064283 | OakACRV1 |
| Ocimum alphacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064284 | OciACRV1 |
| Panicum betacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064328 | PanBCRV1 |
| Passiflora betacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064329 | PasBCRV1 |
| peat soil associated betacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064330 | PSaBCRV1 |
| peat soil associated betacytorhabdovirus 2 | BK064331 | PSaBCRV2 |
| Pelargonium alphacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064285 | PelACRV1 |
| Pentaphragma betacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064332 | PenBCRV1 |
| Phellodendron betacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064333 | PheBCRV1 |
| Phyllostachys alphacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064286 | PhyACRV1 |
| Pinellia alphacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064287 | PinACRV1 |
| Plumbago necrotic spot associated virus | OR335651 | PNSaV |
| Pogostemom alphacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064288 | PogACRV1 |
| Pogostemom alphacytorhabdovirus 2 | BK064291 | PogACRV2 |
| Pogostemom alphacytorhabdovirus 3 | BK064292 | PogACRV3 |
| Populus betacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064334 | PopBCRV1 |
| Primula alphacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064294 | PriACRV1 |
| Primula alphacytorhabdovirus 2 | BK064295 | PriACRV2 |
| Pueraria betacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064335 | PueBCRV1 |
| Rhopalocnemis gammacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064359 | RhoGCRV1 |
| rose alphacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064296 | RosACRV1 |
| Rubus alphacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064297 | RubACRV1 |
| Schiedea betacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064338 | SchBCRV1 |
| Scutellaria alphacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064298 | ScuACRV1 |
| Sesamum betacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064336 | SesBCRV1 |
| Silene gammacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064360 | SilGCRV1 |
| Sophora betacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064339 | SopBCRV1 |
| Tolmiea alphacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064299 | TolACRV1 |
| Trifolium betacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064340 | TriBCRV1 |
| Triticum alphacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064300 | TriACRV1 |
| Utricularia alphacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064301 | UtrACRV1 |
| Vicia betacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064341 | VicBCRV1 |
| wetland metagenome associated alphacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064302 | WMaACRV1 |
| Wurfbainia alphacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064303 | WurACRV1 |
| Zanthoxylum betacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064342 | ZanBCRV1 |
| Zanthoxylum betacytorhabdovirus 2 | BK064343 | ZanBCRV2 |
| Zanthoxylum betacytorhabdovirus 3 | BK064344 | ZanBCRV3 |
| Zea alphacytorhabdovirus 1 | BK064304 | ZeaACRV1 |
Virus names and virus abbreviations are not official ICTV designations.
* Coding region sequence incomplete

