Family: Geminiviridae
Genus: Turncurtovirus
Distinguishing features
Turncurtoviruses have a genome arrangement in the complementary-sense similar to that of curtoviruses (consisting of four overlapping genes) but only two open reading frames in the virion-sense (the curtoviruses have three ORFs). The complementary-sense genes are homologous to those of curtoviruses but show little sequence identity to their curtovirus homologs, with the exception of the product of the C4 open reading frame (ORF). The virion-sense predicted product of the V2 ORF of turncurtoviruses shows no significant similarity with any proteins in public databases, whereas the product of the V1 ORF (encoding the capsid protein of geminiviruses) shows low levels of sequence identity to curtovirus coat proteins (CP).
Virion
See discussion under family description.
Genome organization and replication
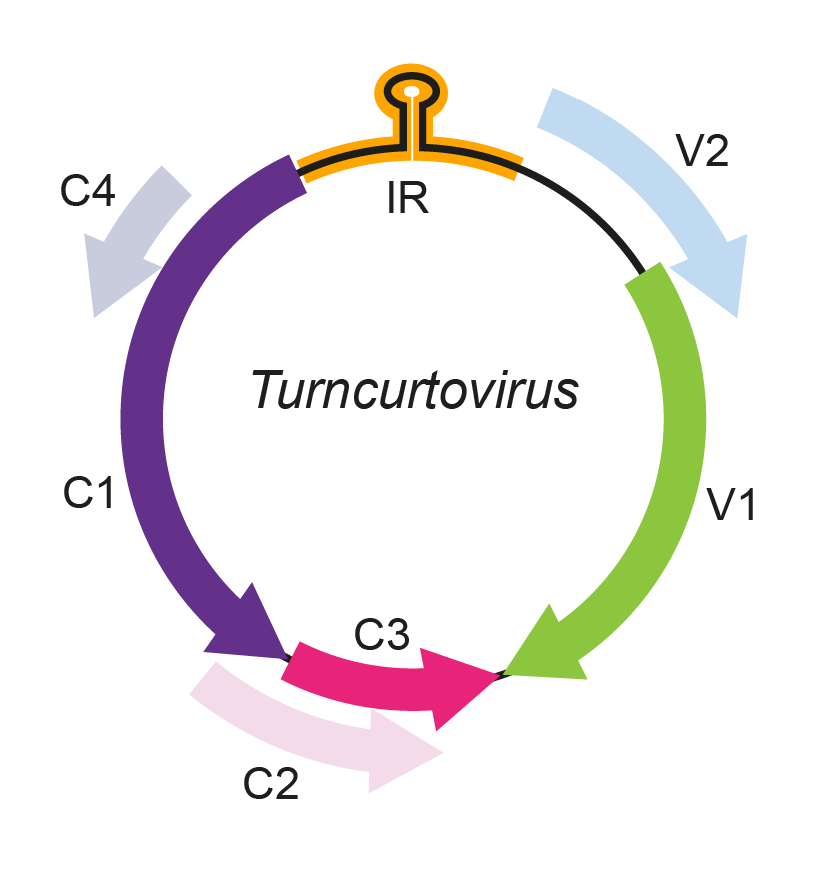
Turncurtovirus genomes contain six ORFs (Figure 1. Turncurtovirus), which are positionally similar to those of other geminiviruses: two in the virion-sense (V1 and V2) and four in the complementary-sense (C1, C2, C3 and C4). This arrangement differs from the curtoviruses in having two rather than three virion-sense genes and from the mastreviruses in having four rather than two complementary-sense genes (Varsani et al., 2014b). The turnip curly top virus (TCTV) V1 gene encodes a geminivirus-like CP that is most similar to, but clearly distinct from, those of all presently characterised curtoviruses. The C1 ORF encodes a homologue of replication-associated protein (Rep), involved in the initiation of rolling-circle replication. The TCTV Rep is most closely related to the Rep of the curtovirus beet curly top virus. Within the N-terminal region of the Rep protein of TCTV, the sequence of the iteron-related domain (proposed to be involved in recognition of the replication origin) is unique to this virus. All the other proteins that TCTV potentially encodes are notably divergent when compared to their becurtovirus and curtovirus homologues. For the V2 product, no significant sequence similarity can be identified to any other geminivirus protein or any other sequences in the databases (Briddon et al., 2010). All characterized TCTV isolates have the same 5′-TAATATTAC-3′ nonanucleotide sequence motif that is found at the virion-strand origins of replication of mastreviruses, begomoviruses, curtoviruses and topocuviruses (Kamali et al., 2016).
|
|
|
Figure 1. Turncurtovirus. Genomic organization of turncurtoviruses. ORFs are denoted as either being encoded on the virion-sense (V) or complementary-sense (C) strand. The position of the stem-loop containing the conserved 5′-TAATATTAC-3′ sequence located in the intergenic region (IR) is shown. |
Biology
Host range
TCTV has a narrow host range, with only Brassica rapa (turnip) and Raphanus sativus (radish) reported as symptomatic hosts. The weeds Descurainia sophia (herb sophia), Anchusa sp. (bugloss), Solanum americanum (black nightshade) and Hibiscus trionum (flower of an-hour) have been reported as symptomless hosts (Razavinejad et al., 2013). Turnip curly top virus (TLRV) naturally infects turnip, radish, lettuce, beet and basil (Kamali et al., 2016). Sesame curly top virus has been identified from sesame and from the leafhopper Circulifer haematoceps collected from sesame plants (Hasanvand et al., 2018).
Transmission
TCTV and TLRV can be transmitted from infected plants to healthy turnip seedlings by the leafhopper Circulifer haematoceps under laboratory conditions (Razavinejad et al., 2013, Kamali et al., 2016).
Species demarcation criteria
Based on the distribution of nucleotide sequence pairwise identities, a species demarcation threshold of 80% and a strain demarcation threshold of 95% are currently used (Varsani et al., 2014b, Kamali et al., 2016). Thus, pairs of turncurtovirus full genome sequences with >80% pairwise identity are considered as members of the same species and full-genome sequences that have >95% pairwise identity should be considered as members/variants of the same strain. These criteria are tentative. As more turncurtovirus sequences are discovered, this threshold may change.