Family: Phenuiviridae
Genus: Hudovirus
Distinguishing features
Húběi lepidoptera virus 1 (HbLV-1) is assigned to Hudovirus lepidopteris, the only species in the genus. Hudovirus RNA was found by high-throughput sequencing of RNA from a pool of butterflies sampled in Húběi (湖北省), China. The hudovirus genome has four genes, encoding a large protein (L), two external glycoproteins (Gn and Gc), and a nucleocapsid protein (N). Based on well-supported Maximum Likelihood or Maximum Clade Credibility trees inferred from complete L protein sequences, viruses classified in the genus Hudovirus form a monophyletic cluster clearly distinguished from other phenuivirids. There currently is no cultured hudovirus isolate (Shi et al., 2016).
Virion
Morphology
Virion morphology is unknown. Based on the putative proteins encoded by the virus genome, the virion is probably a spherical or pleomorphic virion with the enveloped structure.
Nucleic acid and Protein
The hudovirus genome encompasses three segments of negative-sense RNA, namely L (7.5 kb), M (5.1 kb) and S (1.3 kb). The terminal nucleotides of each segment occur in a canonical, conserved sequence (in coding sense) 5′-ACACAAAGAC… GUCUUUGUGU-3′ and may form panhandle structures typical of other members of the class Bunyaviricetes (Table 2 Phenuiviridae). All three genomic RNAs contain untranslated regions flanking a single ORF which, based on comparisons with other negative-sense RNA viruses, is predicted to be contained in the virus-complementary strand. In silico analysis of hudovirus putative ORF sequences suggests that the hudovirus genome encodes three structural proteins: L with a predicted molecular mass of 275 kDa, a glycoprotein precursor of 163 kDa and N of 31 kDa, all of which share sequence homology and/or structural characteristics with the cognate proteins of other phenuivirids (Table 3 Phenuiviridae).
Genome organization and replication
Hudovirus genome arrangement is similar to that of beidiviruses, citriciviruses, goukoviruses, hudiviruses, phasiviruses, pidchoviruses and tanzaviruses (Figure 1 Hudovirus). The L, M and S segments putatively encode L, a glycoprotein precursor (comprising Gn and Gc) and N, respectively. The Gn and Gc glycoproteins of 107 kDa and 55 kDa were earlier referred to as G1 and G2 based on apparent size following gel electrophoresis. The hudovirus genome does not encode the non-structural proteins NSs or NSm. Details of virus replication are unknown (Shi et al., 2016).
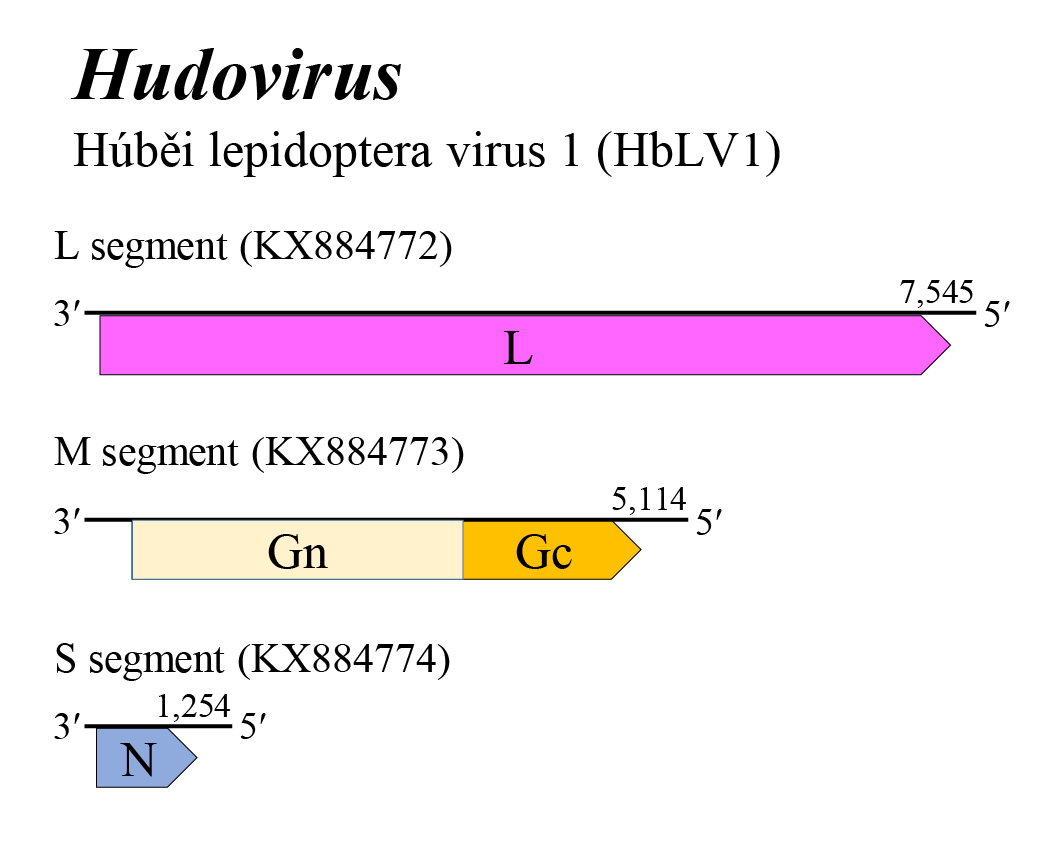 |
| Figure 1 Hudovirus. Genome organization of a hudovirus. Coloured boxes depict ORFs that encode N, nucleocapsid protein; Gn and Gc, external glycoproteins; and L, large protein. |
Biology
Hudoviruses have been detected in a pool of Lepidoptera sampled in China (Shi et al., 2016).
Species demarcation criteria
Not defined as the genus currently includes only a single species.

