Family: Caulimoviridae
Genus: Vaccinivirus
Distinguishing features
Blueberry fruit drop-associated virus (BFDaV) is a member of the only species in the genus Vaccinivirus. The genome of BFDaV has a single ORF, like that of Petunia vein clearing virus (PVCV), a member of the type species of the genus Petuvirus. However, BFDaV and PVCV are paraphyletic and sequence identity between the polyproteins encoded by BFDaV and PVCV is very low (14.82%). Additionally, the genome of BFDaV is 2,644 bp larger than that of PVCV, with 2,056 bp of this accounted for by a larger intergenic region.
Virion
Virions are unknown.
Nucleic acid
The genome of BFDaV is composed of double stranded DNA, circular, and at 9,850 bp, is the largest known in the family Caulimoviridae.
Genome organization and replication
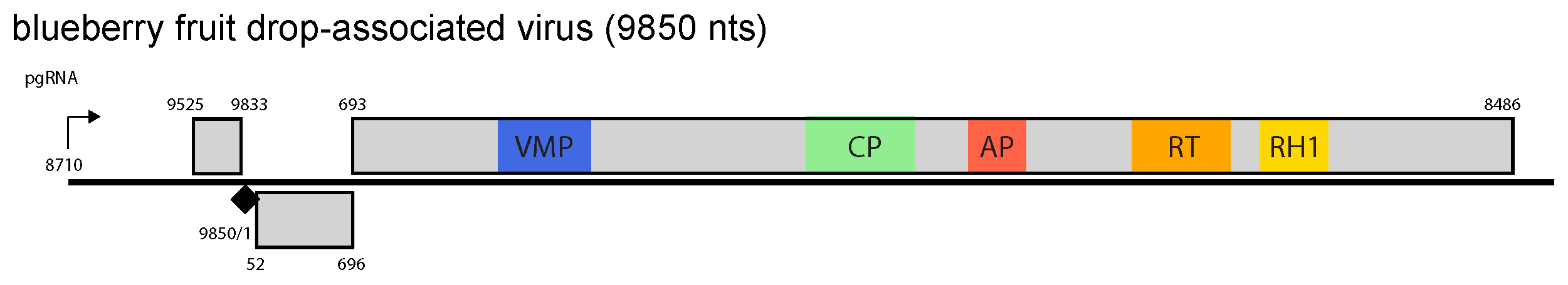
The genome of BFDaV has a single ORF encoding a large polyprotein with movement protein, coat protein, aspartate protease and ribonuclease H domains (Figure 1.Vaccinivirus).
 |
|
Figure 1. Vaccinivirus. Vaccinivirus genome organization. The linearized map begins at the pgRNA transcription start site (black arrow, mapped or predicted ca. 32 nts downstream of TATA box; see (Pooggin et al., 1999)and references therein). The numbering begins from the first nucleotide of the Met-tRNA primer binding site (black diamond). Light grey boxes mark open reading frames (ORFs). Conserved protein domains as listed in the Pfam database (http://xfam.org) are coloured: blue is the viral movement protein (VMP) (PF01107), red is the retropepsin (pepsin-like aspartic protease) (AP) (CD00303), orange is the reverse transcriptase (RT) (CD01647) and yellow is the RNase H1 (RH1) (CD06222). The conserved C-terminus of the coat protein (CP) is marked green. |
Biology
The only known host of BFDaV is Vaccinium corymbosum.
Derivation of names
Vaccinivirus: derived from Vaccinium corymbosum the binomial name of blueberry, host to the members of the type species
Species demarcation criteria
BFDaV is the sole member of the genus.

