Family: Caulimoviridae
Genus: Rosadnavirus
Distinguishing features
Rose yellow vein virus (RYVV), a member of the only species in the genus, is distinguishable from all other members of the Caulimoviridae by its unique genome organization, in having overlapping ORFs 1, 2 and 3, a very large genome and in its phylogenetic placement based upon analysis of polymerase gene sequences.
Virion
Morphology
Virions of RYVV are icosahedral, 42–45 nm in diameter.
Nucleic acid
Virions contain a single molecule of non-covalently closed circular dsDNA of 9.3 kbp.
Genome organization and replication
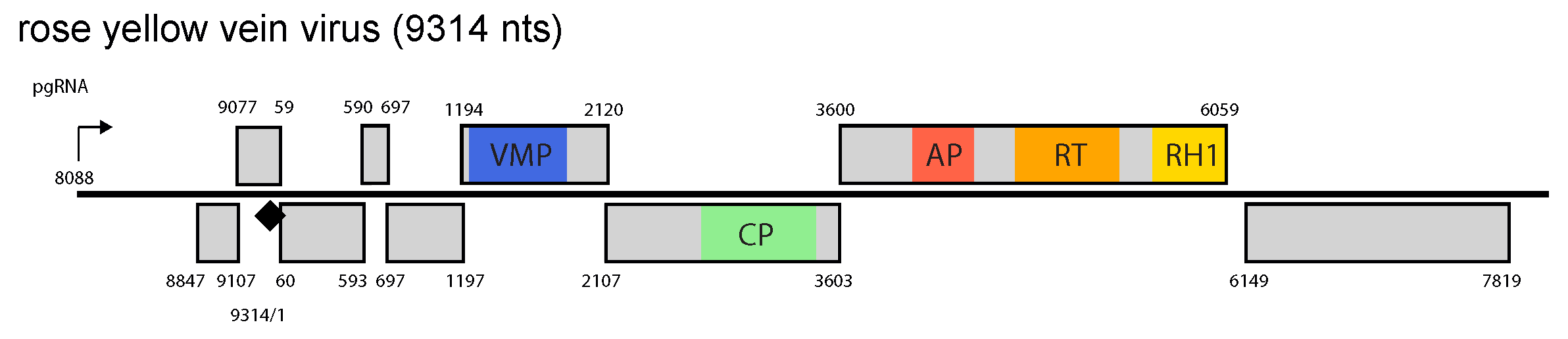
RYVV has the second largest genome of all members in the family Caulimoviridae, and has eight putative ORFs (Mollov et al., 2013) (Figure 1.Rosadnavirus). However, RYVV also differs from members of other genera in having no ORF occurring between the ORFs that encode the movement protein (MP) and capsid protein (CP). Furthermore, RYVV is unique amongst the caulimovirids in having overlapping ORFs 1, 2 and 3. RYVV has no homologue of the caulimovirus/soymovirus aphid transmission factor (ATF). Ribosome shunting and reinitiation of translation on the polycistronic pgRNA of RYVV are assumed to be utilized for gene expression (Pooggin and Ryabova 2018).
 |
|
Figure 1. Rosadnavirus. Rosadnavirus genome organization. The linearized map begins at the pgRNA transcription start site (black arrow, mapped or predicted ca. 32 nts downstream of TATA box; see (Pooggin et al., 1999) and references therein). The numbering begins from the first nucleotide of the Met-tRNA primer binding site (black diamond). Light grey boxes mark open reading frames (ORFs). Conserved protein domains as listed in the Pfam database (http://xfam.org) are colored: blue is the viral movement protein (VMP) (PF01107), red is the retropepsin (pepsin-like aspartic protease) (AP) (CD00303), orange is the reverse transcriptase (RT) (CD01647) and yellow is the RNase H1 (RH1) (CD06222). The conserved C-terminus of the coat protein (CP) is marked green. |
Biology
The virus has only been reported in rose (Rosa spp.). It is responsible for foliar disease of cultivated roses. It is graft but not aphid or mechanically transmissible.
Derivation of names
Rosadnavirus: derived from rosa DNA virus, where Rosa is the generic epithet of rose and DNA refers to the composition of the virus genome.
Species demarcation criteria
RYVV is the sole member of the genus.

