Subfamily: Firstpapillomavirinae
Genus: Deltapapillomavirus
Distinguishing features
These viruses are associated with fibropapillomas in their respective ungulate hosts. Trans-species transmission occurs, where it induces non-productive sarcoids. The E5 protein, located in the region between the early and late genes, has transforming properties.
Virion
See discussion under family description.
Genome organization and replication
See discussion under family description.
Biology
See discussion under family description.
Species demarcation criteria
Putative novel papillomavirus genome with complete genome sequence data available and that is <70% related to papillomaviruses within the genus (Figure 1. Deltapapillomavirus).
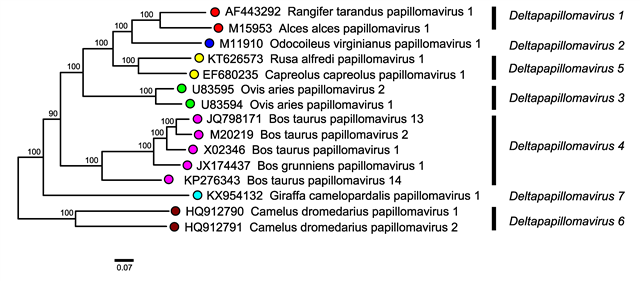 |
| Figure 1. . Deltapapillomavirus. Phylogenetic tree of members of the genus Deltapapillomavirus. The E1, E2, L2, and L1 nucleotide sequences of 343 papillomavirus isolates including representatives of all species and genera within the Papillomaviridae family were aligned as amino acid sequences using MUSCLE v7.221 (Edgar 2004). JModeltest2 (Darriba et al., 2012) was used to determine the optimal model of evolution (GTR + I + G) for the concatenated nucleotide sequences. Maximum likelihood (ML) trees were constructed using RAxML MPI v8.2.9 (Stamatakis 2006) implementing the GTR substitution model. ML bootstrap analysis used the autoMRE-based stopping criterion in RAxML. Following tree construction (tree available in the Resources section of the Papillomaviridae Report), the subtree corresponding to the genus Deltapapillomavirus was isolated. Tips are labelled with virus names and accession numbers; nodes are labelled with bootstrap support values. |

