Family: Potyviridae
Genus: Potyvirus
Distinguishing features
The largest genus in the family contains viruses transmitted by aphids in a non-persistent manner.
Virion
Morphology
Virions are flexuous filaments, 680–900 nm long and 11–13 nm wide, with helical symmetry and a pitch of about 3.4 nm. Particles of some viruses are longer in the presence of divalent cations than in the presence of EDTA.
Physicochemical and physical properties
Virion Sedimentation coefficient S20,w is 137–160S; density in CsCl is 1.31 g cm−3; Extinction coefficient E0.1%1 cm, 260 nm=2.4–2.7.
Nucleic acid
Virions contain a single molecule of linear, positive-sense ssRNA of 9.7–11 kb with a 3′poly(A) terminus; virions contain 5% RNA by weight.
Proteins
Virions contain a single CP of 30–47 kDa. The CP of most isolates of the species Potato virus Y contains 267 aa.
Genome organization and replication
The genome structure potato virus Y, a representative potyvirus, is illustrated in Figure 1.Potyvirus. Members of the subgroup of sweet potato potyviruses encode an additional ORF, PISPO (pretty interesting sweet potato potyvirus ORF) embedded within the C-terminal part of an exceptionally large P1 protein. A transcriptional slippage mechanism leads to production of a trans-frame protein, P1N-PISPO, that functions as an RNA silencing suppressor (Li et al., 2012, Mingot et al., 2016, Olspert et al., 2016, Untiveros et al., 2016) (Figure 1.Potyvirus). The P1 and CP of the sweet potato potyviruses sweet potato virus G (SPVG) and sweet potato virus 2 (SPV2) are significantly large, with the SPVG CP as the largest among the all known species of the genus Potyvirus.
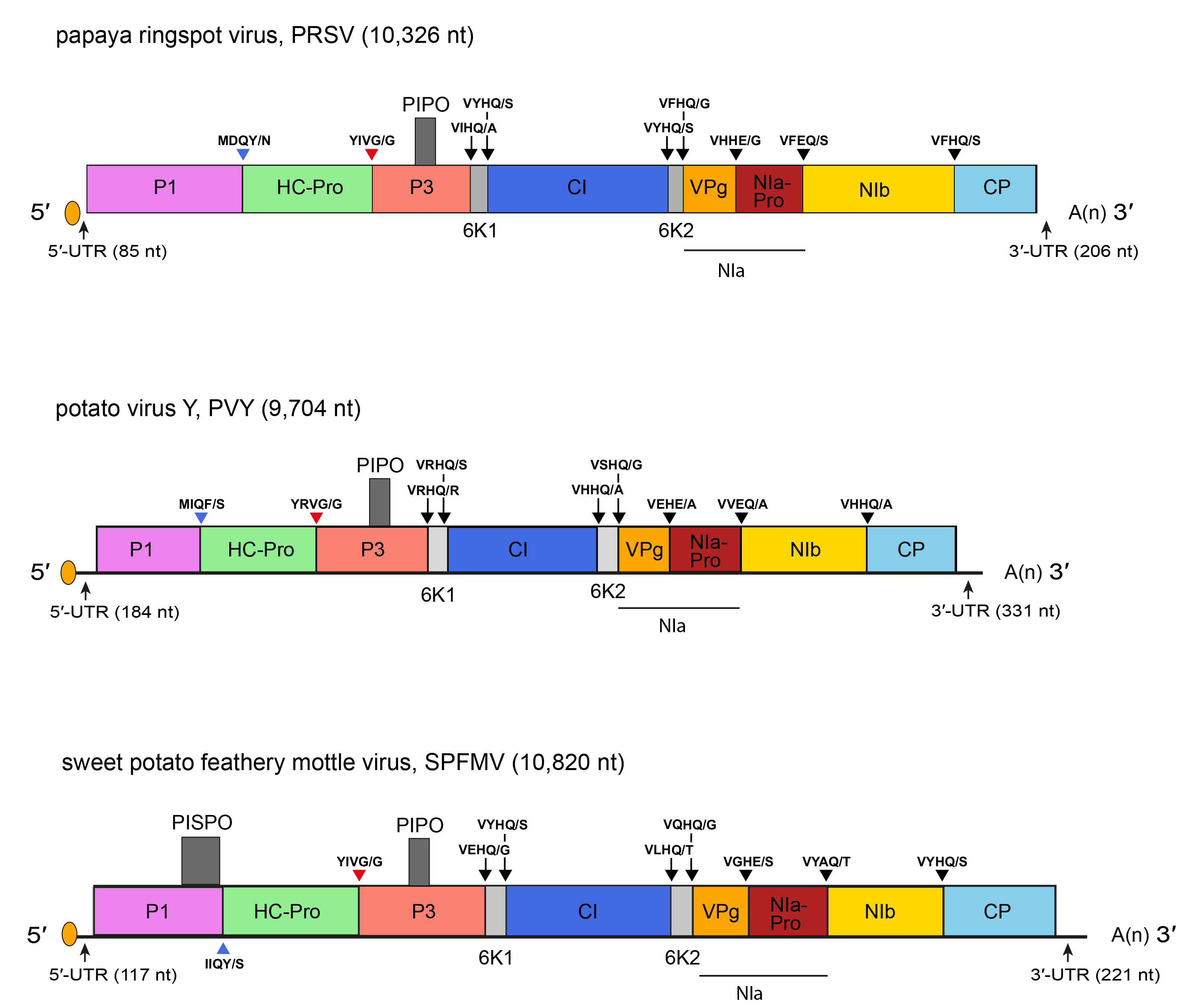 |
| Figure 1.Potyvirus. Schematic diagrams of the potyviruses potato virus Y (PVY), a typical member of the genus Potyvirus, papaya ringspot virus (PRSV) and sweet potato feathery mottle virus (SPFMV) genomes. The ssRNA genome is represented by a line and the polyprotein ORF by an open box with the mature proteolytic products named. The untranslated regions (UTR) are represented by lines on each end of the large ORF. Conventions are as for the potyvirid genome organization map (Figure 2.Potyviridae). The pretty interesting Potyviridae protein (PIPO) and pretty interesting sweet potato potyvirus ORF (PISPO) are represented by small boxes. Not to scale. |
Biology
Many individual viruses have a narrow host range, but a few infect plant species in up to 30 host families. The viruses are transmitted by aphids in a non-persistent manner and are transmissible experimentally by mechanical inoculation. Some isolates are inefficiently transmitted by aphids and others are not transmissible by aphids at all. This is apparently due to mutations within the helper component and/or CP cistrons. Some viruses are seed-transmitted.
Antigenicity
Virions are moderately immunogenic; there are serological relationships among many members. Some monoclonal antibodies react with most aphid-transmitted potyviruses. The CP aa sequence identity among aphid-transmitted viruses is 40–70%. Some viruses are serologically related to viruses in the genera Rymovirus and Bymovirus.
Species demarcation criteria
See discussion under family description.
Member species
The Member Species table enumerating important virus exemplars classified under each species of the genus is provided at the bottom of the page.
Related, unclassified viruses
|
Virus name |
Accession number |
Virus abbreviation |
|
Ammi majus latent virus |
AMLV |
|
|
Anemone mosaic virus |
AnMV |
|
|
Arisaema potyvirus 1 |
ArV1 |
|
|
Arisaema potyvirus 2 |
ArV2 |
|
|
Bermuda grass mosaic virus |
BGMV |
|
|
Bermuda grass southern mosaic virus |
BGSMV |
|
|
chickpea yellow mosaic virus |
CpYMV |
|
|
Clitoria chlorosis virus |
ClCV |
|
|
Commelina mild mosaic virus |
CMMV |
|
|
cotyledon virus Y |
CotVY |
|
|
Delphinium vein-clearing virus |
DeVCV |
|
|
lily virus A |
LVA |
|
|
melon vein-banding mosaic virus |
MVbMV |
|
|
Muscari mosaic virus |
MMV |
|
|
Omphalodes virus Y |
OmVY |
|
|
ornamental onion stripe mosaic virus |
OOSMV |
|
|
Ornithogalum necrotic mosaic virus |
ONMV |
|
|
Ornithogalum virus 4 |
OV4 |
|
|
Passiflora foetida virus Y |
PfVY |
|
|
siratro 1 virus Y |
S1VY |
|
|
siratro 2 virus Y |
S2VY |
|
|
snowdrop virus Y |
SVY |
|
|
Stenomesson mosaic virus |
StMV |
|
|
Tricyrtis virus Y |
TrVY |
|
|
Trillium crinkled leaf virus |
TCLV |
|
|
Triteleia mosaic virus |
TrMV |
|
|
Veltheimia mosaic virus |
VelMV |
|
|
Veltheimia virus Y |
VelVY |
Virus names and virus abbreviations are not official ICTV designations.
* incomplete genome sequence

