Family: Filoviridae
Genus: Tapjovirus
Distinguishing features
Tapajós virus (TAPV) is the only classified tapjovirus. Tapjoviruses are the only filovirids known to infect reptiles. Notably, tapjoviruses are closely related to piscine striaviruses but have the genomic organization of mammalian filovirids, albeit with five, rather than 1 (orthomarburgviruses), 2–3 (orthoebolaviruses) or 4 (cuevaviruses, dianloviruses) gene overlaps (Horie 2021).
Virion
Virions are unknown.
Nucleic acid
Virions are assumed to contain one or several copies of the linear negative-sense RNA genome that are encapsidated independently.
Proteins
Tapjoviruses likely express at least seven proteins, all of which (nucleoprotein [NP], polymerase cofactor [VP35], matrix protein [VP40], glycoprotein [GP1,2], transcriptional activator [VP30], ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex-associated protein (VP24), and large protein [L]) are homologs of proteins expressed by mammalian filovirids (Horie 2021). After VP40, the second most abundant structural protein in a tapjovirion is assumed to be NP, which encapsidates the tapjovirus genome. The least abundant protein is assumed to be L, which mediates tapjovirus genome replication and transcription.
Genome organization and replication
The tapjovirus genome has the gene order 3′-NP-VP35-VP40-GP-VP30-VP24-L-5′ (Horie 2021) (Figure 1.Tapjovirus). The undetermined extragenic sequences at the extreme 3′-end (leader) and 5′-end (trailer) of the genome are assumed to be conserved and partially complementary. The transcriptional initiation and termination (polyadenylation) sites have yet to be identified.
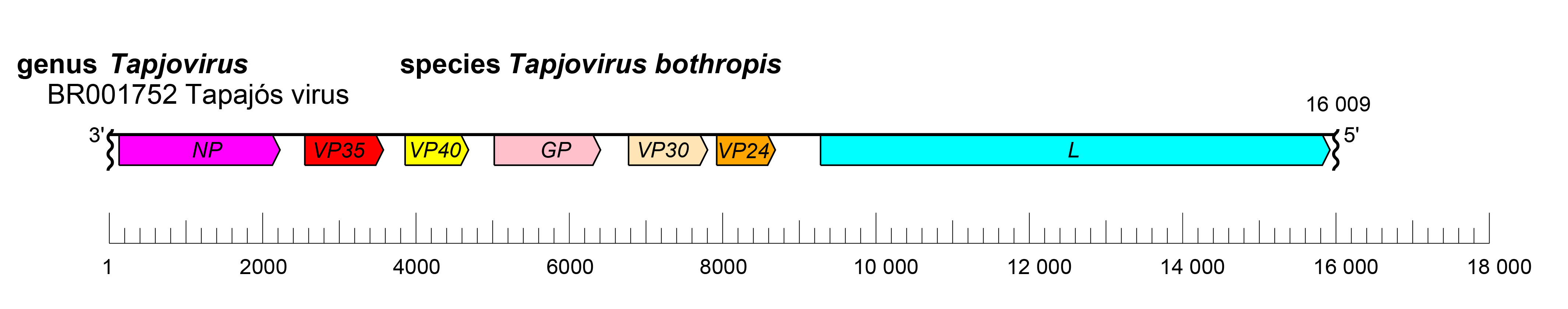 |
| Figure 1. Tapjovirus. Schematic representation of the tapjovirus genome organization, drawn to scale. GP, glycoprotein gene; L, large protein gene; NP, nucleoprotein gene; VP24, ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex-associated protein; VP30, transcriptional activator gene; VP35, polymerase co-factor gene; VP40, matrix protein gene. Wavy lines indicate incomplete genome ends. |
The replication strategy of tapjoviruses remains to be studied.
Biology
Tapjoviruses were discovered during a metagenomic analysis of a fer-de-lance (viperid Bothrops atrox (Linnaeus, 1758)) caught in Brazil (Horie 2021).
Species demarcation criteria
The genus currently includes only a single species.

