Subfamily: Agantavirinae
Genus: Agnathovirus
Distinguishing features
Wēnlǐng hagfish virus (WEHV) is the only classified agnathovirus. WEHV infects myxinid fish (Shi et al., 2018).
Virion
Virions are unknown.
Nucleic acid
Agnathoviruses have tri-segmented negative-sense RNA genomes of about 14.6 kb (small [S] segment: 3.0 kb; medium [M] segment: 4.8 kb; large [L] segment: 6.8 kb) (Shi et al., 2018).
Proteins
Based on sequence data only, agnathoviruses likely express three structural proteins: nucleoprotein (N), glycoprotein precursor (GPC), and large protein (L) (Shi et al., 2018).
Genome organization and replication
The S segment encodes N, the M segment encodes GPC, and the L segment encodes L (Figure 1 Agnathovirus). Agnathovirus genomic segments are expected to assume circular forms via non-covalent binding of complementary and conserved 3′- and 5′-terminal sequences.
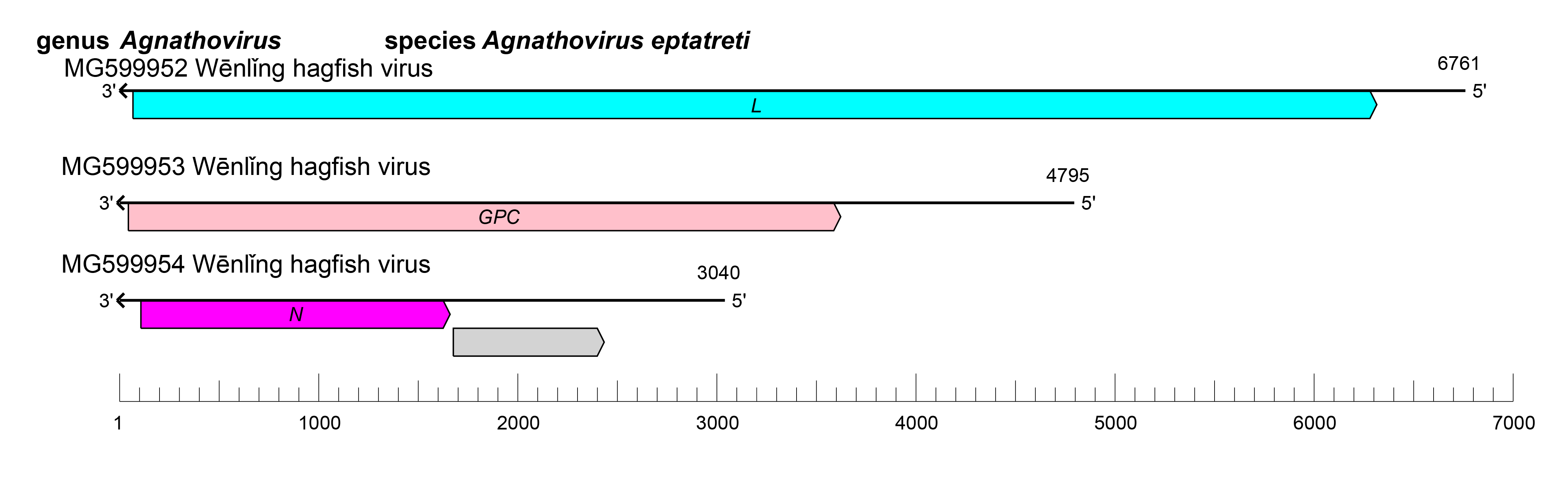 |
| Figure 1 Agnathovirus. Schematic representation of agnathovirus genome organization. The 5′- and 3′-ends of each segment (S, M and L) are, by analogy to other hantavirids, predicted to be complementary at their termini, likely promoting the formation of circular ribonucleoprotein complexes within the virion. |
Biology
WEHV infects inshore hagfish (myxinid Eptatretus burgeri (Girard, 1855)) in China (Shi et al., 2018). Replication-competent agnathovirus isolates have not yet been obtained, and hence agnathovirus biology remains to be elucidated.
Species demarcation criteria
The genus currently only includes a single species.

