Subfamily: Actantavirinae
Genus: Percilovirus
Distinguishing features
Luposicya lupus actinovirus (LlAV) and and Wēnlǐng yellow goosefish virus (WEYGV) are the only classified perciloviruses. These viruses infect actinopterygian fish (Costa et al., 2023, Shi et al., 2018).
Virion
Virions are unknown.
Physicochemical and physical properties
Not reported.
Nucleic acid
Perciloviruses have tri-segmented negative-sense RNA genomes of about 10.6–12.3 kb (small [S] segment: 1.0–2.0 kb; medium [M] segment: 3.4–3.9 kb; large [L] segment: 6.2–6.4 kb) (Costa et al., 2023, Shi et al., 2018).
Proteins
Based on sequence data only, perciloviruses likely express three structural proteins: nucleoprotein (N), glycoprotein precursor (GPC), and large protein (L) (Costa et al., 2023, Shi et al., 2018).
Genome organization and replication
The S segment encodes N, the M segment encodes GPC, and the L segment encodes L (Figure 1 Percilovirus). Percilovirus genomic segments are expected to assume circular forms via non-covalent binding of complementary and conserved 3′- and 5′-terminal sequences.
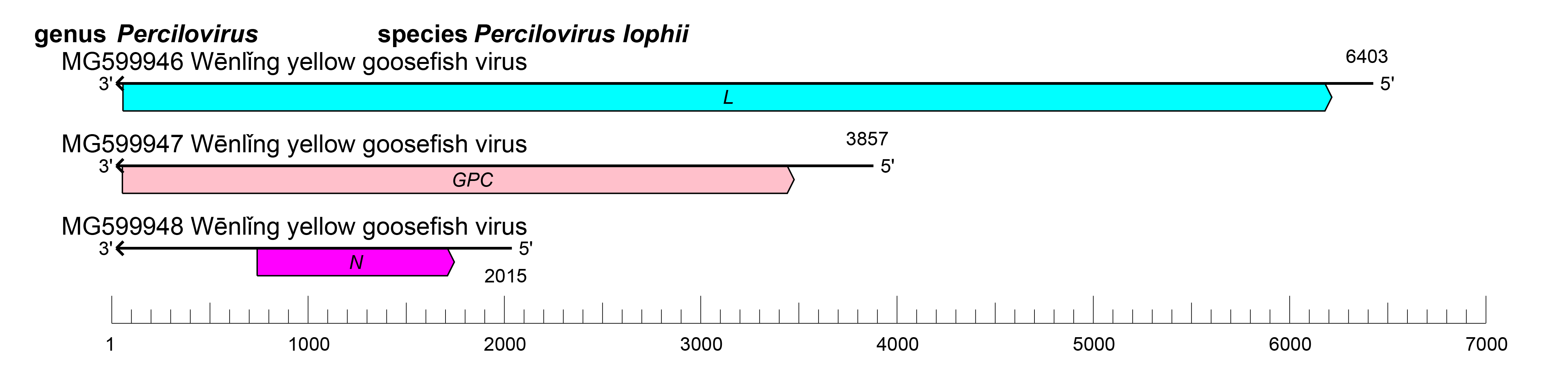 |
| Figure 1 Percilovirus. Schematic representation of percilovirus genome organization. The 5′- and 3′- ends of each segment (S, M and L) are, by analogy to other hantavirids, predicted to be complementary at their termini, likely promoting the formation of circular ribonucleoprotein complexes within the virion. |
Biology
Luposicya lupus actinovirus (LlAV) infect wolfsnout goby (gobiid Luposicya lupus J. L. B. Smith, 1959) in Australia (Costa et al., 2023) and Wēnlǐng yellow goosefish virus (WEYGV) infect yellow goosefish (lophiid Lophius litulon D. S. Jordan, 1902) in China (Shi et al., 2018). Replication-competent percilovirus isolates have not yet been obtained, and hence percilovirus biology remains to be elucidated.
Species demarcation criteria
Demarcation of species is based upon DivErsity pArtitioning by hieRarchical Clustering (DEmARC) analysis) using concatenated deduced S, M, and L segment expression product sequences (Laenen et al., 2019).

