Family: Lispiviridae
Jun-Min Li (李俊敏), Fei Wang (王飞), Zhuang-Xin Ye (叶庄新), Gongyin Ye (叶恭银) and Sofia Paraskevopoulou (Σοφία Παρασκευοπούλου)
The citation for this ICTV Report chapter is the summary published as:
Corresponding authors: Jun-Min Li (李俊敏):[email protected] and Sofia Paraskevopoulou (Σοφία Παρασκευοπούλου):[email protected]
Edited by: Jens H. Kuhn and Stuart G. Siddell
Posted: June 2023, July 2024, May 2025
Summary
Lispiviridae is a family for viruses with negative-sense RNA genomes of 6.5–15.5 kb (Table 1 Lispiviridae). The family includes 30 genera and 45 species. Most members of this family have been identified within arthropod hosts sampled in Africa, America, Asia, Europe, and Oceania. The viruses are only known from their genome sequences.
Table 1 Lispiviridae. Characteristics of members of the family Lispiviridae
| Characteristic | Description |
| Example | Anisopteromalus calandrae negative-strand RNA virus 2 (MW864603), species Anicalvirus hangzhouense |
| Virion | Unknown |
| Genome | 6.5–15.5 kb of negative-sense RNA |
| Replication | Unknown |
| Translation | Unknown |
| Host range | Arthropods and nematodes of the superphylum Ecdysozoa |
| Taxonomy | Realm Riboviria, kingdom Orthornavirae, phylum Negarnaviricota, class Monjiviricetes, order Mononegavirales; 30 genera and 45 species |
Virion
Morphology
Unknown.
Nucleic acid
A single molecule of linear, negative-sense RNA of 6.5–15.5 kb.
Genome organization and replication
Genomes of members of the family Lispiviridae commonly have five to six open reading frames (ORFs) (Figure 1 Lispiviridae). Encoded proteins likely include a glycoprotein and a large protein (L) including an RNA directed RNA polymerase (RdRP) domain.
 |
| Figure 1 Lispiviridae. Genome organization of members of each genus in the family Lispiviridae. ORFs are indicated as boxes, coloured according to the predicted protein function (G, glycoprotein; L, large protein including an RNA-directed RNA polymerase (RdRP) domain; N, nucleoprotein; P, predicted phosphoprotein; M, predicted matrix protein). The GenBank accession numbers for genome sequences of exemplar viruses for each species are shown to the left of the virus names. |
Biology
Members of the family Lispiviridae have been detected in arthropods (hemipterans, odonatans, hymenopterans, orthopterans and arachnids), nematodes, mammals (mice) and bird faeces (Table 2 Lispiviridae), sampled in Asia (China, Thailand), Africa (Gabon), Europe (Spain, Germany, Netherlands) and Oceania (New Zealand, Australia) (Viljakainen et al., 2018, Käfer et al., 2019, Williams et al., 2019, Lay et al., 2020, Chiapello et al., 2021, Huang et al., 2021, Wang et al., 2021, Ye et al., 2022, Zhu et al., 2022, Aragão et al., 2023, Dong et al., 2024).
Table 2 Lispivirdae. Hosts of lispivirids.
| Virus genus | Virus | Host species |
| Acridvirus | Hángzhōu acrida cinerea lispivirus 1 | Short-horned grasshoppers (Acrididae: Acrida cinerea) |
| Aleyavirus | Bemisia tabaci arlivirus 1 | Whiteflies (Aleyrodidae: Bemisia tabaci) |
| Aleybvirus | Bemisia tabaci arlivirus 2 | Whiteflies (Aleyrodidae: Bemisia tabaci) |
| Anicalvirus | Anisopteromalus calandrae negative-strand RNA virus 2 | Parasitoid wasps (Pteromalidae: Anisopteromalus calandrae ) |
| Anicalvirus | hymenopteran arli-related virus OKIAV100 | Parasitoid wasps (Pteromalidae: Orussus unicolor) |
| Anidravirus | Anisopteromalus calandrae negative-strand RNA virus 1 | Parasitoid wasps (Pteromalidae: Anisopteromalus calandrae ) |
| Aranavirus | Guìyáng lispivirus 1 | Orb-weaver spiders (Araneidae: Argiope bruennichi) |
| Aranbvirus | Guìyáng lispivirus 2 | Orb-weaver spiders (Araneidae: Argiope bruennichi) |
| Arlivirus | Lĭshì spider virus 2 | Spiders (Araneae) |
| Arlivirus | Nbu stink bug virus 1 | Stink bugs (Pentatomidae: Erthesina fullo) |
| Arlivirus | Hángzhōu scotinophara lurida lispivirus 1 | Stink bugs (Pentatomidae: Scotinophara lurida) |
| Avesvirus | Arlivirus sp. virus | [bird] |
| Artemvirus | brine shrimp arlivirus 1 | Brine shrimps (Artemia sp.) |
| Artemvirus | brine shrimp arlivirus 2 | Brine shrimps (Artemia sp.) |
| Artemvirus | brine shrimp arlivirus 3 | Brine shrimps (Artemia sp.) |
| Artemvirus | brine shrimp arlivirus 4 | Brine shrimps (Artemia sp.) |
| Artemvirus | brine shrimp arlivirus 5 | Brine shrimps (Artemia sp.) |
| Artemvirus | brine shrimp arlivirus 6 | Brine shrimps (Artemia sp.) |
| Artemvirus | brine shrimp arlivirus 8 | Brine shrimps (Artemia sp.) |
| Birfecvirus | Arlivirus sp. XZN142933 | [bird] |
| Canmovirus | Pedras lispivirus | Mosquitoes (Sabethes quasicyaneus) |
| Copasivirus | isopteran arli-related virus OKIAV103 | Termites (Termitidae: Occasitermes) and subterranean termites (Rhinotermitidae: Coptotermes) |
| Copasivirus | isopteran arli-related virus OKIAV103 | Termites (Termitidae: Occasitermes) and subterranean termites (Rhinotermitidae: Coptotermes) |
| Copasivirus | Jimsystermes virus | Termites (Termitidae: Occasitermes) |
| Coroavirus | blattodean arli-related virus OKIAV101 | Egyptian cockroach (Polyphaga aegyptiaca) |
| Cybitervirus | coleopteran arli-related virus OKIAV107 | Diving beetles (Dytiscidae: Cybister lateralimarginalis) |
| Damravirus | Húběi odonate virus 10 | Dragonflies and damselflies (Odonata sp.) |
| Damravirus | Fǔshùn ischnura senegalensis lispivirus 1 | Damselflies (Coenagrionidae: Ischnura senegalensis) |
| Ganiavirus | Fùyùn tick virus 1 | Ticks |
| Ganiavirus | Tǎchéng tick virus 6 | Soft ticks (Argasidae: Argas miniatus) |
| Hemipvirus | Hángzhōu eysarcoris guttigerus lispivirus 1 | Stink bugs (Pentatomidae: Eysarcoris guttigerus) |
| Hemipvirus | Hángzhōu cletus punctiger lispivirus 1 | Leaf-footed bugs (Coreidae: Cletus punctiger) |
| Leocovirus | Húběi rhabdo-like virus 3 | Beetles (Coleoptera sp.) |
| Nematovirus | Wǔchāng romanomermis nematode virus 2 | Nematodes (Mermithidae: Romanomermis sp.) |
| Phelinovirus | hymenopteran arli-related virus OKIAV99 | Parasitoid wasps (Aphelinidae: Aphelinus abdominalis) |
| Rivapovirus | hemipteran arli-related virus OKIAV94 | Whiteflies (Aleyrodidae: Trialeurodes vaporariorum) |
| Robevirus | Hángzhōu lispivirus 1 | Rove beetles (Paederus fuscipes) |
| Sanstrivirus | Sānxiá water strider virus 4 | Water striders (Gerridae sp.) |
| Stylovirus | strepsipteran arli-related virus OKIAV104 | Insect endoparasites of bees (Stylopidae: Stylops melittae) |
| Supelovirus | blattodean arli-related virus OKIAV102 | Wood cockroaches (Ectobiidae: Supella longipalpa) |
| Synelinevirus | hymenopteran arli-related virus OKIAV98 | Gall wasps (Cynipidae: Synergus umbraculus) |
| Synelinevirus | Linepithema humile rhabdo-like virus 1 | Ants (Formicidae: Linepithema humile) |
| Weflthvirus | Frankliniella occidentalis associated mononegavirales virus 1 | Western flower thrips (Frankliniella occidentalis) |
| Usmuvirus | Amsterdam virus | [True mice (Muridae: Mus musculus)] |
| Xenophyvirus | hemipteran arli-related virus OKIAV95 | Moss bugs (Peloridiidae: Xenophyes metoponcus) |
Hosts in brackets may not be the natural host.
Derivation of names
Acridvirus: from the grasshopper family Acrididae. The species epithet hangzhouense derives from Hángzhōu (杭州市), China, the sample location for Hangzhou acrida cinerea lispivirus 1.
Aleyavirus: from the whitefly family Aleyrodidae, with an added “a” to distinguish it from Aleybvirus. The species epithet fuyangense derives from Fùyáng (阜阳市), China, the sampling location for Bemisia tabaci alrivirus 1.
Aleybvirus: from the whitefly family Aleyrodidae, with an added “b” to distinguish it from Aleyavirus. The species epithet fuyangense derives from Fùyáng (阜阳市), China, the sampling location for Bemisia tabaci alrivirus 2.
Anicalvirus: from the parasitoid wasp species Anisopteromalus calandrae. The species epithet hangzhouense derives from Hángzhōu (杭州市), China, the sample location for Anisopteromalus calandrae negative-strand RNA virus 2. The species epithet hesdarense derives from Darmstadt, Hesse, Germany, the sample location for hymenopteran arli-related virus OKIAV100.
Anidravirus: from the parasitoid wasp species Anisopteromalus calandrae. The species epithet hangzhouense derives from Hángzhōu (杭州市), China, the sample location for Anisopteromalus calandrae negative-strand RNA virus 1.
Aranavirus: from the spider family Araneidae with an added “a” to distinguish it from Aranbvirus. The species epithet guiyangense derives from Guìyáng (贵阳市), China, the sample location for Guìyáng lispivirus 1.
Aranbvirus: from the spider family Araneidae with an added “b” to distinguish it from Aranavirus. The species epithet guiyangense derives from Guìyáng (贵阳市), China, the sample location for Guìyáng lispivirus 2.
Arlivirus: from the class Arachnida and the city Lǐshì (李市). The species epithet arachnae derives from the class Arachnida, including spiders, the epithet ningboense derives from Níngbō (宁波市), China, the sample location for Nbu stink bug virus 1 and the epithet hangzhouense from Hángzhōu (杭州市), China, the sample location for Hángzhōu scotinophara lurida lispivirus 1.
Artemvirus: from the shrimp family Artemiidae. The species epithet bsafialis is derived from the virus name brine shrimp arlivirus 1 (first), the species epithet bsasecalis is derived from the virus name brine shrimp arlivirus (second), the species epithet bsathalis is derived from the virus name brine shrimp arlivirus 3 (three), the species epithet bsafalis is derived from the virus name brine shrimp arlivirus 4 (four), the species epithet bsafivalis is derived from the virus name brine shrimp arlivirus 5 (five), the species epithet bsasialis is derived from the virus name brine shrimp arlivirus (six) and the species epithet bsaeighalis is derived from the virus name brine shrimp arlivirus 8 (eight).
Avesvirus: from the class Aves. The species epithet sinense derives from “sino-”, the prefix for China, that being the sample location for Arlivirus sp. virus isolate YSN1024.
Birfecvirus: after bird and fecal. The species epithet tibetense is derived from Tibet, China, the discovery location of Arlivirus sp. XZN142933.
Canmovirus: after canopy mosquitoes. The species epithet mahaense is derived from the place of sampling, Maranhao
Copasivirus: from the host genera Coptotermes and Occasitermes. The species epithet cattienense derives from Cát Tiên National Park, Vietnam, the sample location for Cát Tiên Hospitalitermes lispi-like virus, the epithet ivindoense derives from Ivindo National Park, Gabon, the sample location for isopteran arli-related virus OKIAV103 and the epithet manlyvaleense from Manly Vale, New South Wales, Australia, the sampling location for Jimsystermes virus.
Coroavirus: after cockroach. The species epithet germense is derived from the place of sampling, Germany.
Cybitervirus: from Cybister lateralimarginalis. The species epithet niederense derives from the German word “nieder” meaning “low”, as a reference to “Lower Saxony”, Lüchow-Dannenberg, Lower Saxony, Germany being the sampling location for coleopteran arli-related virus OKIAV107.
Damravirus: from odonate damselflies and dragonflies. The species epithet dentatis derives from dentatum, the Latin word for toothed (odonate is derived from ὀδούς, the Greek word for tooth) and the epithet fushunense from Fǔshùn (抚顺市), China, the sample location for Fǔshùn ischnura senegalensis lispivirus 1.
Ganiavirus: from Argas miniatus. The species epithet fuyunense derived from Fùyùn County (富蕴县) of Xīnjiāng Uygur Autonomous Region, China, the sample location for Fùyùn tick virus 1, and the epithet tachengense is derived from Tǎchéng (塔城) Prefecture, China, the sample location for Tǎchéng tick virus 6.
Hemipvirus: from Hemiptera. The species epithet scuti is derived from the Latin scutum meaning “shield” and the epithet veri from the Latin verus, meaning “true”, the Cletus being a genus of true bugs.
Leocovirus: from a scrambled contraction of Coleoptera. The species epithet coleopteris derives from Coleoptera.
Lispiviridae: from Lĭshì spider virus 2.
Nematovirus: from nematode. The species epithet wuchangense derives from Wǔchāng (武昌) District, China, the sampling location for Wǔchāng romanomermis nematode virus 2.
Phelinovirus: derived from Aphelinus abdominalis. The species epithet aphidis derives from aphid in reference to the use of Aphelinus abdominalis wasps as biological control agents for aphid pests of agricultural crops.
Rivapovirus: from Trialeurodes vaporariorum. The species epithet aleyrodidae is derived from the host whitefly family, Aleyrodidae.
Robevirus: after rove beetles. The species epithet hanzense is derived from the place of sampling, Hángzhōu.
Sanstrivirus: from Sānxiá water strider virus 4. The species epithet gerridis is derived from the host family name Gerridae.
Stylovirus: from the host genus Stylops. The species epithet niederense is derived from the German word “nieder” meaning “low”, as a reference to “Lower Saxony”, Lüchow-Dannenberg, Lower Saxony, Germany being the sampling location for strepsipteran arli-related virus OKIAV104.
Supelovirus: from the host Supella longipalpa. The species epithet thailandense derives Thailand, the sample location for blattodean arli-related virus OKIAV102.
Synelinevirus: from the host genus names Synergus and Linepithema. The species epithet bonnense is derived from Bonn, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, the sample location for hymenopteran arli-related virus OKIAV98 and the epithet paranaense is derived from Paraná River, the river in South American that constitutes the native range of Linepithema humile ants that are hosts to Linepithema humile rhabdo-like virus 1.
Usmuvirus: from Mus musculus. The species epithet newyorkense derives from New York, USA, the sampling location for Amsterdam virus.
Weflthvirus: after western flower thrips. The species epithet itaense is derived from the place of sampling, Italy.
Xenophyvirus: from the host genus Xenophyes. The species epithet mathesonense is derived from Lake Matheson, South Island Westland District, New Zealand, the sampling location for hemipteran arli-related virus OKIAV95.
Genus demarcation criteria
Members of different genera in the family are < 50% identical in a coding-complete RdRP amino acid sequence.
Species demarcation criteria
Members of different species in the same genus are <85% identical in a coding-complete RdRP amino acid sequence.
Relationships within the family
Phylogenetic relationships of members of the family Lispiviridae are shown in Figure 2 Lispiviridae.
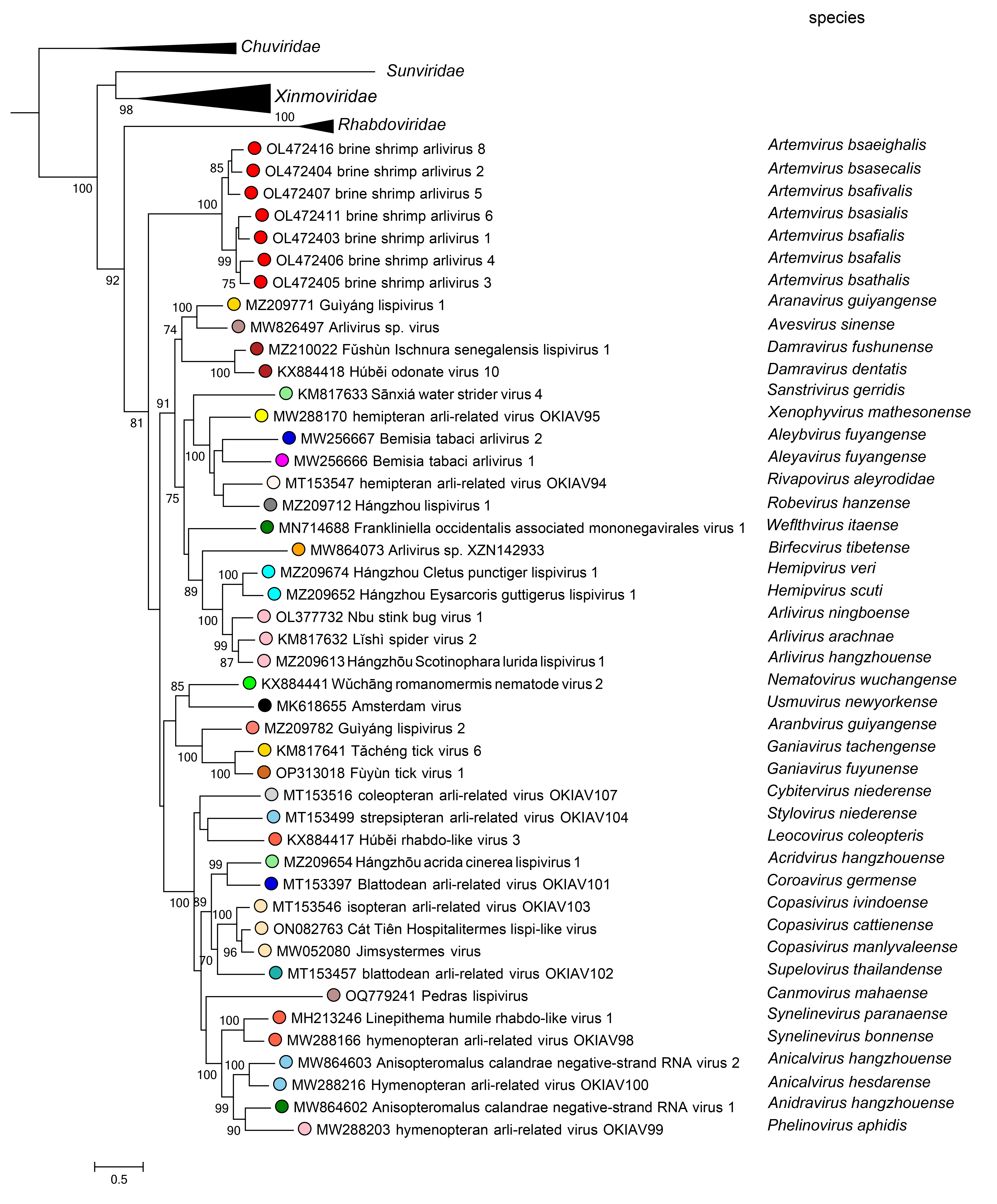 |
| Figure 2 Lispiviridae. Phylogenetic relationships of viruses in the family Lispiviridae. The phylogenetic tree is based on a MAFFT-alignment of the RdRP amino acid sequences using the L-INS-i algorithm and was inferred using ModelTest-NG and the LG substitution model. Numbers on branch nodes represent transfer bootstrap expectation values (1,000 replicates). |
Relationships with other taxa
The viruses in the family Lispiviridae have a similar genome organisation with other members of the order Mononegavirales.
Related, unclassified viruses
| Virus name | Accession number | Virus abbreviation |
| megalopteran arli-related virus OKIAV106 | MT153449 | MARV106 |
| neuropteran arli-related virus OKIAV105 | MW288169 | NARV105 |
| bat faecal associated arli-like virus 1 | ON872577 | BFAALV1 |
Virus names and virus abbreviations are not official ICTV designations.

