Family: Solemoviridae
Genus: Sobemovirus
Distinguishing features
Sobemoviruses have a polycistronic, positive-sense RNA genome that consists of non-coding 5′- and 3′-regions and 4–5 ORFs. ORFs 1, x, 2a and 2b are all translated from the genomic RNA (Figure 1. Sobemovirus). Translation of ORFx and ORF2a occur via a leaky scanning mechanism. The RNA-directed RNA polymerase (RdRP) encoded by ORF2b is expressed as a fusion protein through a −1 ribosomal frameshift mechanism. The 3′-proximal ORF3 is translated from a subgenomic RNA.
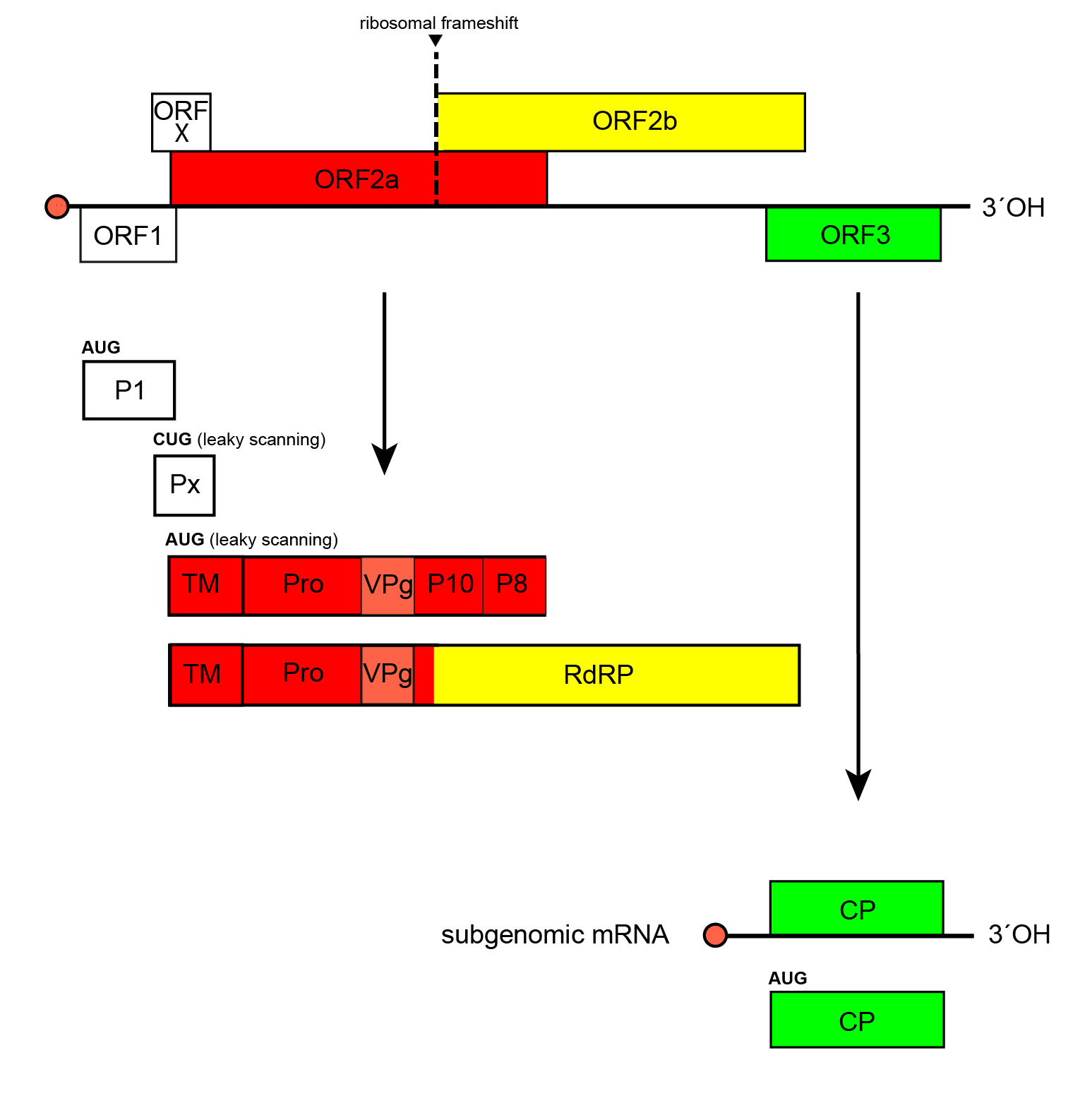 |
| Figure 1. Sobemovirus Transcriptional and translational map of the genome of southern bean mosaic virus (genus Sobemovirus). Open reading frames (ORFs) are indicated by their position above the genome in the order -1, 0 and +1; those with sequence homology at the family level are represented by coloured boxes, while those with no sequence homology are shown colourless. P1, protein P1; Px, protein X; TM, transmembrane domain; Pro, serine protease domain; VPg, virus protein genome-linked; P10, protein P10; P8, protein P8; RdRP, RNA-directed RNA polymerase; CP, coat protein. |
Virion
Morphology
See discussion under family description.
Physicochemical and physical properties
Virions usually sediment as a single band in CsCl but form two or more bands in Cs2SO4 gradients. The virion Mr is about 6.6×106; S20,w is about 115; buoyant density is about 1.36 g cm−3 in CsCl. Virions are stabilized by divalent cations, pH-dependent protein-protein interactions and salt bridges between protein and viral RNA. Virions swell in EDTA and at alkaline and neutral pH.
Nucleic acid
Genomes are 3,983 nt for sowbane mosaic virus and 4,547 nt for imperata yellow mottle virus. See further discussion under family description.
Proteins
See discussion under family description.
Genome organization and replication
See discussion under family description.
Biology
See discussion under family description.
Species demarcation criteria
Species are distinguished by the host range of member viruses combined with analysis of their genome sequences. The threshold for species demarcation based on complete genome sequences is <75% nucleotide identity between viruses belonging to different species. Serological relatedness between viruses may help in distinguishing species.

