Family: Phasmaviridae
Genus: Orthophasmavirus
Distinguishing features
There are 21 classified orthophasmaviruses. These viruses are associated with blattodean, coleopteran, dipteran, hemipteran, hymenopteran, and odonatan insects (Ballinger et al., 2014, Li et al., 2015, Schoonvaere et al., 2016, Shi et al., 2016, Makhsous et al., 2017, Shi et al., 2017, Käfer et al., 2019, Öhlund et al., 2019, Batson et al., 2021, Truong Nguyen et al., 2022, Zhang et al., 2022, Matsumura et al., 2024).
Virion
Virions are unknown.
Nucleic acid
Orthophasmaviruses have tri-segmented negative-sense RNA genomes of about 9.7–12.4 kb (small [S] segment: 1.3–2.9 kb; medium [M] segment: 2.1–2.8 kb; large [L] segment: 6.3–6.9 kb) (Ballinger et al., 2014).
Proteins
Orthophasmaviruses express three structural proteins (nucleoprotein (N), glycoprotein precursor (GPC), and large protein (L)), two nonstructural proteins (NSs and NSm), and an unnamed protein (Käfer et al., 2019).
Genome organization and replication
The S segment encodes N, and in some cases, NSs and an unnamed protein, the M segment encodes GPC and NSm, and the L segment encodes L protein (Ballinger et al., 2014, Käfer et al., 2019) (Figure 1 Orthophasmavirus). Orthophasmavirus genomic segments are expected, by analogy with other bunyaviricetes, to assume circular ribonucleoprotein complexes within the virion via non-covalent binding of complementary and conserved 3′- and 5′-terminal sequences. Complementary terminal sequences for the three segments of Kigluaik phantom virus (KIGV) are 5′-AGCAGCACG (Ballinger et al., 2014).
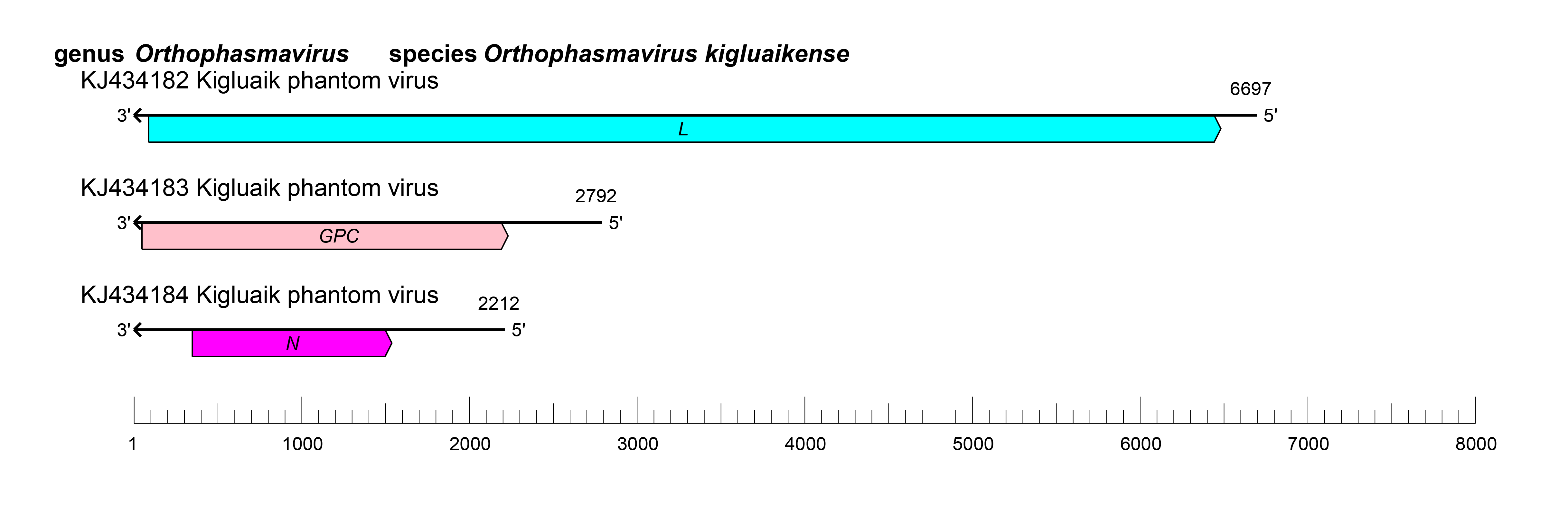 |
| Figure 1 Orthophasmavirus. Schematic representation of orthophasmavirus genome organization. L: gene encoding L protein; GPC, gene encoding GPC; N: gene encoding N protein. |
Biology
Orthophasmaviruses are associated with phantom midges (chaoborid Chaoborus spp.), mosquitoes (culicid Aedes spp., Anopheles spp., Culex spp., Mansonia spp., Ochlerotatus spp.), European orchard bees (megachilid Osmia cornuta (Latreille, 1805)), wasps (chrysidid Chrysis spp. and Philoctetes spp.), green pugs (geometrid Pasiphila rectangulata (Linnaeus, 1758)), lady beetles (coccinellid Harmonia axyridis (Pallas, 1773)), true bugs (delphacid Laodelphax striatellus (Fallén, 1826)), German cockroaches (ectobiid Blattella germanica Linnaeus, 1767), and unspecified odonates (Ballinger et al., 2014, Li et al., 2015, Schoonvaere et al., 2016, Shi et al., 2016, Makhsous et al., 2017, Shi et al., 2017, Käfer et al., 2019, Öhlund et al., 2019, Batson et al., 2021). Putative orthophasmaviruses are associated with culicid mosquitoes and tephritid fruit flies (Truong Nguyen et al., 2022, Zhang et al., 2022, Matsumura et al., 2024). Orthophasmavirids are widely distributed and RNA has been detected in insects throughout North and South America, Europe, and Asia. Although orthophasmaviruses have not been isolated and the biology not defined, the viruses are thought to be restricted to insects and to require insect host-specific replication factors.
Species demarcation criteria
The orthophasmavirus species demarcation criterion is <95% identity in the amino acid sequence of the L protein.
Related, unclassified viruses
| Virus name | Accession number | Virus abbreviation | Reference |
| Anopheles stephensi orthophasmavirus | L: LC775043; M: LC775044; S: LC775045 | AsOV | (Matsumura et al., 2024) |
| Bactrocera latifrons orthophasmavirus | L: MW310369; M: MW310370; S: MW310371 | (Zhang et al., 2022) | |
| Fǔshùn phasmavirus 3 | L: MZ210032; S: MZ210033 | ||
| Hämeenlinna orthophasmavirus 1 | L: ON955160* | (Truong Nguyen et al., 2022) | |
| Hämeenlinna orthophasmavirus 2 | L: ON955164* | (Truong Nguyen et al., 2022) | |
| Kuusamo orthophasmavirus 1 | L: ON955166* | (Truong Nguyen et al., 2022) | |
| Kuusamo orthophasmavirus 2 | L: ON955167* | (Truong Nguyen et al., 2022) | |
| Kuusamo orthophasmavirus 3 | L: ON955168* | (Truong Nguyen et al., 2022) | |
| Kuusamo orthophasmavirus 4 | L: ON955169* | (Truong Nguyen et al., 2022) | |
| Lestijärvi orthophasmavirus 1 | L: ON955171* | (Truong Nguyen et al., 2022) | |
| Lestijärvi orthophasmavirus 2 | L: ON955172* | (Truong Nguyen et al., 2022) | |
| Sanya phasmavirus 1 | L: MZ209824 | ||
| Sanya phasmavirus 2 | L: MZ209825; M: MZ209826 |
Virus names and virus abbreviations are not official ICTV designations.

