Family: Phasmaviridae
Genus: Hymovirus
Distinguishing features
Hymenopteran phasma-related virus OKIAV252 (HyHV1) and hymenopteran phasma-related virus OKIAV250 (HyHV2) are the only classified hymoviruses. These viruses are associated with hymenopteran insects (Käfer et al., 2019).
Virion
Virions are unknown.
Nucleic acid
Hymoviruses have tri-segmented negative-sense RNA genomes of about 12.3–12.4 kb (small [S] segment: 1.5–1.6 kb; medium [M] segment: 4.2 kb; large [L] segment: 6.6 kb) (Käfer et al., 2019).
Proteins
Based on sequence data, hymoviruses express three structural proteins: nucleoprotein (N), glycoprotein precursor (GPC), and large protein (L), as well as two nonstructural proteins, NSs and NSm (Käfer et al., 2019).
Carbohydrates
Not reported.
Genome organization and replication
The S segment encodes N and NSs, the M segment encodes GPC and NSm, and the L segment encodes L protein (Käfer et al., 2019) (Figure 1 Hymovirus). Hymovirus genomic segments are expected, by analogy with other bunyaviricetes, to assume circular ribonucleoprotein complexes within the virion via non-covalent binding of complementary and conserved 3′- and 5′-terminal sequences.
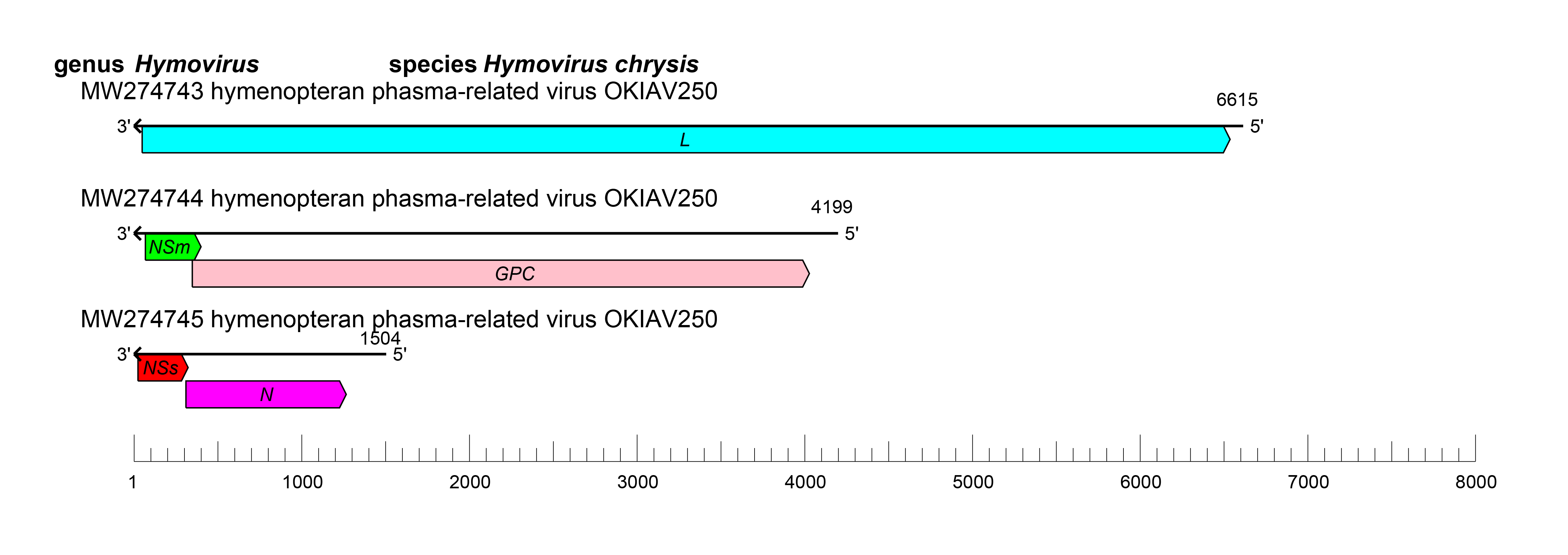 |
| Figure 1 Hymovirus. Schematic representation of hymovirus genome organization. L: gene encoding L protein; GPC, gene encoding GPC; N: gene encoding N protein; NSm: gene encoding NSm; NSs: gene encoding NSs. |
Biology
Hymoviruses are associated with cuckoo wasps (chrysidid Chrysis sp.) in Europe (Käfer et al., 2019). Replication-competent hymovirus isolates have not yet been obtained, and hence hymovirus biology remains to be elucidated.
Species demarcation criteria
The hymovirus species demarcation criterion is <95% identity in the amino acid sequence of the L protein.

