Family: Alphaflexiviridae
Genus: Sclerodarnavirus
Distinguishing features
There is a single species in the genus, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum debilitation-associated RNA virus represented by Sclerotinia sclerotiorum debilitation-associated RNA virus, a capsid-less mycovirus. Despite the lack of capsid, phylogenetic analysis of the replication-associated protein (Rep) places it within the Alphaflexiviridae family (Xie et al., 2006).
Virion
Morphology
None.
Physicochemical and physical properties
No information.
Nucleic acid
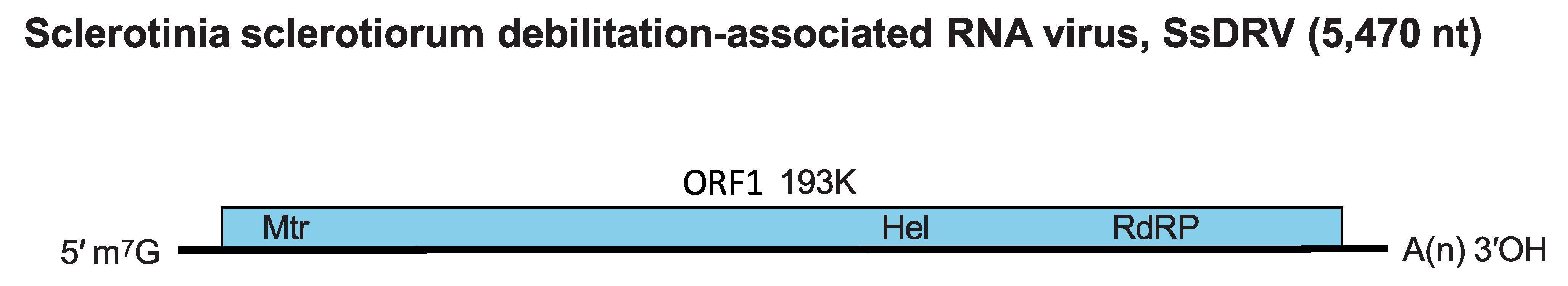
A single linear molecule of positive-sense RNA of 5470 nt with a polyadenylated tract at the 3′-terminus (Figure 1. Sclerodarnavirus).
Proteins
No information available.
Carbohydrates
Not applicable.
Genome organization and replication
There is a single ORF encoding a Rep protein of 193 kDa (Figure 1. Sclerodarnavirus).
 |
|
Figure 1. Sclerodarnavirus. Sclerotinia sclerotiorum debilitation-associated RNA virus genome organization. Mtr, methyltransferase; Hel, helicase; RdRP, RNA-directed RNA polymerase. |
Biology
Sclerotinia sclerotiorum debilitation-associated RNA virus was discovered in the plant pathogenic fungus Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and appears to cause debilitation (hypovirulence).
Derivation of names
Sclerodarna: from Sclerotinia sclerotiorum debilitation-associated RNA virus, the type species of the genus.
Species demarcation criteria
Since there is currently only a single species in the genus, species demarcation criteria are not yet defined, but , as delineated for other genera in the family, members of distinct species may have less than 72% nt identity (or 80% aa identity) between Rep genes.

