Family: Alphaflexiviridae
Genus: Botrexvirus
Distinguishing features
Viruses belonging to the single species in the genus infect a filamentous fungus. The virus genome lacks the triple gene block ORFs characteristic of plant-infecting members of the family (Howitt et al., 2006).
Virion
Morphology
Virions are flexuous filaments of 720 nm modal length and about 13 nm in diameter.
Physicochemical and physical properties
No information.
Nucleic acid
Virions of Botrytis virus X (BotVX) contain a single molecule of linear single-stranded RNA of 6966 nt, excluding the 3′-poly(A) tail.
Proteins
The only structural protein of BotVX is the capsid protein composed of 400 aa (43 kDa).
Carbohydrates
None reported.
Genome organization and replication
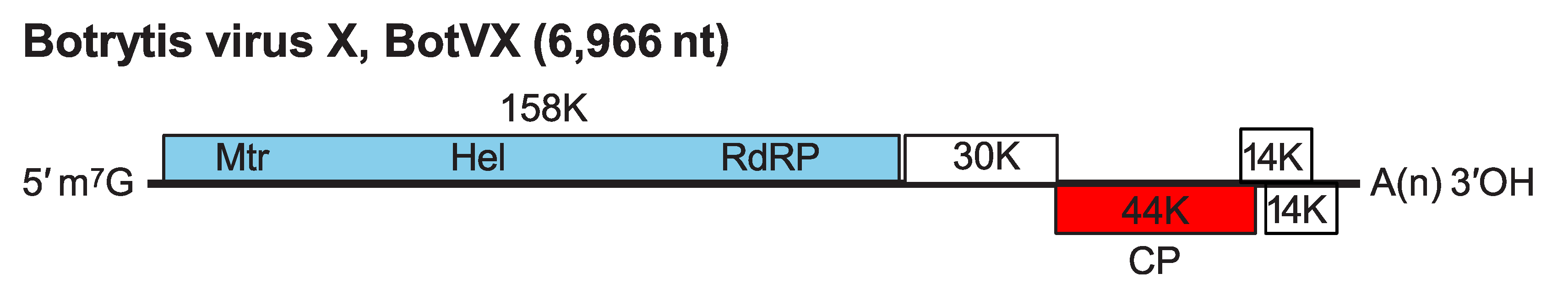
The BotVX genomic RNA contains five putative ORFs on the positive strand, a 5′-UTR of 95 nt and a 3′-UTR of 149 nt, followed by a poly(A) tail (Figure 1. Botrexvirus). ORF1 encodes the 158 kDa replication-associated (Rep) protein, ORF3 encodes the 44 kDa capsid protein (CP) and the functions of the other predicted proteins (ORF2, 30 kDa; ORF4, 14 kDa and ORF5, 14 kDa) are unknown.
 |
|
Figure 1. Botrexvirus. Genome organization of Botrytis virus X showing the relative positions of the ORFs and their expression products. Mtr, methyltransferase; Hel, helicase; RdRP, RNA-directed RNA polymerase; CP, capsid protein. |
Biology
BotVX was discovered infecting an isolate of the plant pathogenic fungus Botrytis cinerea. Its mode of transmission is unknown. The same fungal isolate was also infected with a virus now classified in the species Botrytis virus F (genus Mycoflexivirus, family Gammaflexiviridae).
Derivation of names
Botrex: from Botrytis virus X, the type species in the genus
Species demarcation criteria
Since there is currently only a single species in the genus, species demarcation criteria are not yet defined, but, as delineated for other genera in the family, members of distinct species may have less than 72% nt identity (or 80% aa identity) in their CP or Rep genes.

