Family: Betaflexiviridae (Interim Report)
This is a summary page created by the ICTV Report Editors using information from associated Taxonomic Proposals and the Master Species List.
Edited by: Luisa Rubino
Posted: December 2024
Summary
The family Betaflexiviridae includes ssRNA(+) viruses of plants (Table 1 Betaflexiviridae). The family Betaflexiviridae was established in 2009 (Master Species List #25).
Table 1 Betaflexiviridae. Characteristics of members of the family Betaflexiviridae.
| Characteristic | Description |
| Example | cowpea mild mottle virus (HQ184471), species Carlavirus vignae, genus Carlavirus |
| Virion | Filamentous, 12 nm diameter, 600–1000 nm long (Figure 1 Betaflexiviridae) |
| Genome | ssRNA(+), 1 linear segment, 6.4–9.5 kb, polyadenylated, probably capped (Figure 2 Betaflexiviridae) |
| Replication | Viral factories, involves genome size dsRNA |
| Translation | From genome size and subgenome size mRNAs, proteolytic processing |
| Host range | Plants |
| Taxonomy | Realm Riboviria, kingdom Orthornavirae, phylum Kitrinoviricota, class Alsuviricetes, order Tymovirales: 2 subfamilies, 15 genera, 152 species (Figure 3 Betaflexiviridae) |
 |
 |
| Figure 1 Betaflexiviridae. (Top) Transmission electron micrograph of filamentous particles of cowpea mild mottle virus in sap of symptomatic V. unguiculata subsp. sesquipedalis leaf. Bar: 100 nm. Image from Figure 1 of Brito M, Fernández-Rodríguez T, Garrido MJ, Mejías A, Romano M, Marys E. First report of Cowpea mild mottle Carlavirus on yardlong bean (Vigna unguiculata subsp. sesquipedalis) in Venezuela. Viruses. 2012 Dec 14;4(12):3804-11 under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. (Bottom) Schematic of virion (image modified from ViralZone (viralzone.expasy.org, under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, credit: SwissBioPics). |
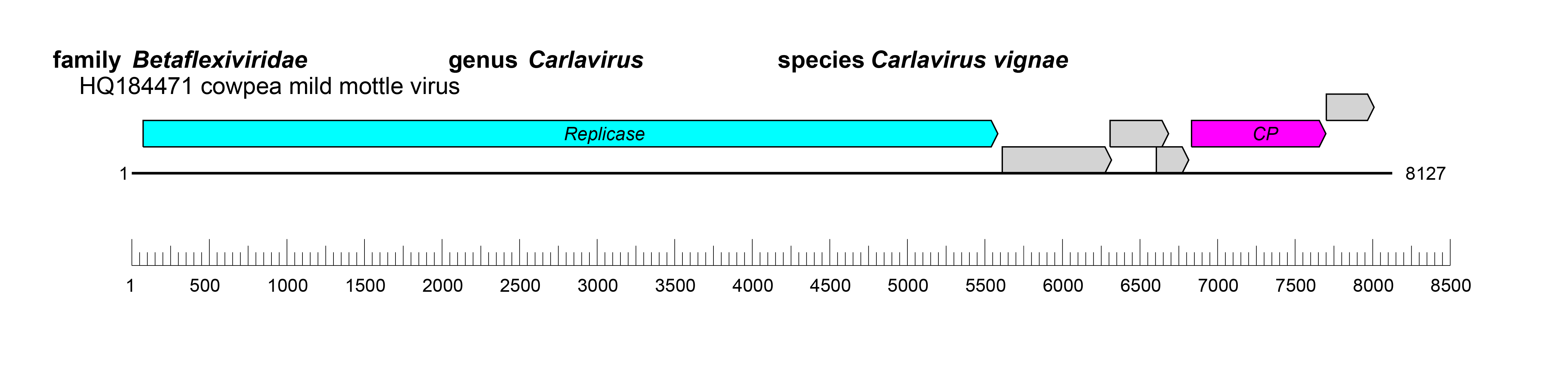 |
| Figure 2 Betaflexiviridae. Genome organisation of cowpea mild mottle virus, a member of the family Betaflexiviridae. Boxes indicate open reading frames as annotated on GenBank accession HQ184471. |
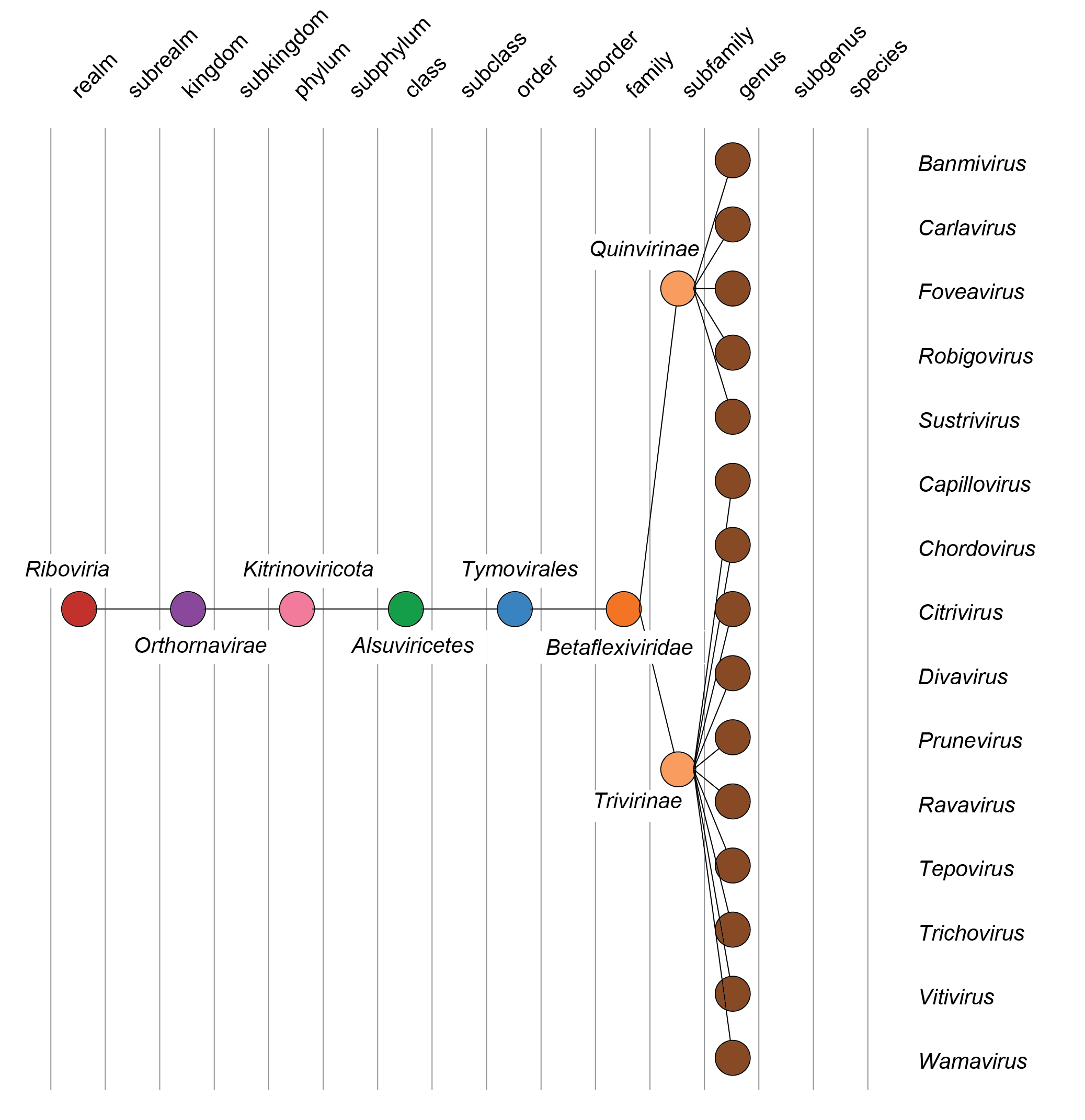 |
| Figure 3 Betaflexiviridae. Taxonomy of the family Betaflexiviridae. For clarity, species are not shown (apart from Banana virus X; a taxonomic proposal to remove this species from the family has been approved and is awaiting ratification); a full list of species in the family is provided in the Member species table at the bottom of this page. |
Derivation of names
Banmivirus: from banana mild mosaic virus
Betaflexiviridae: from the Ancient Greek βῆτα (bêta), the second letter of the Greek alphabet, and flexi, referring to the second family created from the division of the old family Flexiviridae, a group of filamentous and highly flexible viruses; the suffix -viridae for family taxa
Capillovirus: from the Latin capillus, meaning “a hair”
Carlavirus: from carnation latent virus
Chordovirus: from chord, the strings on a harp or other stringed instrument, inf reference to the (presumed) thread-like virions
Citrivirus: from citrus leaf blotch virus
Divavirus: from Diuris virus A
Foveavirus: from the Latin fovea, meaning “pit” or “hole”, relating to a disease symptom of apple stem pitting virus
Prunevirus: from Prunus, the plant genus that is host to the viruses apricot vein clearing-associated virus and Caucasus prunus virus
Ravavirus: from Ribes americanum virus A
Robigovirus: from the Latin robigo, meaning rust, for the rusty symptoms associated with some viruses in the genus, including cherry necrotic rusty mottle virus
Sustrivirus: from sugarcane striate mosaic-associated virus
Tepovirus: from potato virus T
Trichovirus: from the Latin thrix, meaning “hair”
Vitivirus: from Vitis vinifera¸the scientific name of the grapevine, host of grapevine virus A
Wamavirus: from watermelon virus A

