Family: Anelloviridae
Chapter Version: ICTV Ninth Report; 2009 Taxonomy Release
Virion properties
Morphology
Virions are non-enveloped, with reported diameters of about 30 nm for torque teno viruses (TTVs, genus Alphatorquevirus) and torque teno mini viruses (TTMVs, genus Betatorquevirus) (Figure 1).
Physicochemical and physical properties
The buoyant density of virions in CsCl is 1.31–1.33 g cm−3 for TTVs and 1.27–1.28 g cm−3 for TTMVs, both estimated using virus purified from serum.
Nucleic acid
Virions contain a single molecule of circular ssDNA, which ranges from about 2 to about 3.9 kb in size. Genomes are of negative sense. The putative non-coding region generally contains one or two sequences of about 80–110 nt with high G+C content (ca. 90%), which is postulated to form a secondary structure composed of stems and loops. A region of about 130 nt, located in the untranslated part of the genome, is relatively well conserved between members of the family.
Proteins
Two main open reading frames, ORF1 and ORF2, and additional ORFs, may be deduced directly from the nucleotide sequence. These ORFs overlap partially, and their estimated sizes differ widely among isolates. Transfection approaches, restricted to the study of some TTV isolates, have demonstrated that at least 5–7 proteins ranging from about 12 to 80 kDa may be expressed via alternative translational initiation. The ORF1 proteins of human and animal anelloviruses possess arginine-rich, hydrophilic N-terminal sequences, and at least one amino acid sequence motif with which rolling circle replication (RCR) of the virus DNA may be associated. On this basis, ORF1 is believed to encode the putative capsid protein and replication-associated protein of anelloviruses. Hypotheses regarding functions of the other proteins are based on studies involving specific isolates. ORF2, which presents a highly conserved motif, WX7HX3CXCX5H, identifiable in its N-terminal part, may encode a protein with phosphatase activity (TTMVs), or a peptide able to suppress NF-κB pathways (TTVs). ORF3 of TTVs has a serine-rich domain at the C-terminus capable of generating different phosphorylation sites, and might play some role in maintaining persistent viral infection. It was also demonstrated that a short TTV peptide, encoded by the N-terminus of a putative ORF, is able to induce p53-independent apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines.
Lipids
Unknown.
Carbohydrates
Unknown.
Genome organization and replication
Anelloviruses harbour a relatively well conserved genetic organization with a coding region containing a major ORF, ORF1, an overlapping ORF2 and several additional ORFs, and an untranslated region (Figure 2). Knowledge of the genome expression and replication mechanisms remains limited, mainly owing to the lack of an efficient cell culture propagation system. TTV-specific mRNAs have been detected in various tissues and organs in humans, and following transfection studies. At least theree mRNAs of different sizes (ca. 2.9, 1.2 and 1.0 kb) are transcribed from the negative strand of the putative circular ds replicative form TTV DNA. The existence of these mRNAs supports the view that both ORF1 and ORF2 are functional, and also suggests that additional transcripts are generated by complex splicing. The transcription profile of other members of the family is not known, but the fact that they share similar genome organizations is highly suggestive that several mRNAs may be expressed as for TTVs. The presence within ORF1 of conserved amino acid sequence motifs, which occur in the Rep proteins of other animal and plant viruses with circular ssDNA genomes (within Circoviridae and Nanoviridae), suggests that replication of anellovirus DNA may use a rolling circle mechanism of replication.
Antigenic properties
It has been demonstrated that TTV particles in the blood are bound to immunoglobulins G (IgG) and M (IgM), forming immune complexes; they exist as free virions in feces.
Biological properties
Epidemiological studies have demonstrated the global distribution of anelloviruses in rural and urban populations. Their overall prevalence in the general population is high (>90%). Although they were initially suspected of being transmitted only by blood transfusion, the global dispersion of the viruses in populations and their detection in various biological samples (e.g. plasma, saliva and feces) suggests combined modes of diffusion, and in particular the spread by saliva droplets. Other modes of transmission, such as those involving maternal or sexual routes, have also been suggested. The link between anellovirus infection and a specific pathology remains unproven, although some studies suggested possible associations with liver or respiratory diseases, hematological disorders or cancer. The effects of anelloviruses on the immune system are also generally unknown.
Infection with anelloviruses is not restricted to human hosts. Viruses have been detected in non-human primates (chimpanzee, macaque, tamarin and douroucouli), tupaia, pets (cat and dog) and farm animals (pig and cow). Such identifications were recently extended to a marine mammal (sea lion). The analysis of complete viral sequences from different animal sources reveals a high heterogeneity in the size of the viral genome (ca. 2 to 3.9 kb), along with a high genetic divergence when compared with human isolates. However, genomic organization and predicted transcription profiles correspond to those found in human isolates.
Genus Alphatorquevirus
Type species Torque teno virus 1
Distinguishing features
The genus contains viruses identified in humans and non-human primates, with genomes ranging from about 3.6 to 3.9 kb.
Species demarcation criteria in the genus
Based on analysis of ORF1 in its entirety, a cut-off value of 35% nucleotide sequence identity is applied as a demarcation criterion.
List of species in the genus Alphatorquevirus
| Torque teno virus 1 |
|
|
| Torque teno virus 1-TA278 | [AB008394] | (TTV1-TA278) |
| Torque teno virus 2 |
|
|
| Torque teno virus 2-CH71 | [AB049608] | (TTV2-CH71) |
| Torque teno virus 3 |
|
|
| Torque teno virus 3-HEL32 | [AY666122] | (TTV3-HEL32) |
| Torque teno virus 4 |
|
|
| Torque teno virus 4-Pt-TTV6 | [AB041957] | (TTV4-Pt-TTV6) |
| Torque teno virus 5 |
|
|
| Torque teno virus 5-TCHN-C1 | [AF345523] | (TTV5-TCHN-C1) |
| Torque teno virus 6 |
|
|
| Torque teno virus 6-KAV | [AF435014] | (TTV6-KAV) |
| Torque teno virus 7 |
|
|
| Torque teno virus 7-PMV | [AF261761] | (TTV7-PMV) |
| Torque teno virus 8 |
|
|
| Torque teno virus 8-Kt-08F | [AB054647] | (TTV8-Kt-08F) |
| Torque teno virus 9 |
|
|
| Torque teno virus 9-BM1C-18 | [DQ187006] | (TTV9-BM1C-18) |
| Torque teno virus 10 |
|
|
| Torque teno virus 10-JT34F | [AB064607] | (TTV10-JT34F) |
| Torque teno virus 11 |
|
|
| Torque teno virus 11-TCHN-D1 | [AF345524] | (TTV11-TCHN-D1) |
| Torque teno virus 12 |
|
|
| Torque teno virus 12-CT44F | [AB064605] | (TTV12-CT44F) |
| Torque teno virus 13 |
|
|
| Torque teno virus 13-TCHN-A | [AF345526] | (TTV13-TCHN-A) |
| Torque teno virus 14 |
|
|
| Torque teno virus 14-CH65-1 | [AB037926] | (TTV14-CH65-1) |
| Torque teno virus 15 |
|
|
| Torque teno virus 15-TJN01 | [AB028668] | (TTV15-TJN01) |
| Torque teno virus 16 |
|
|
| Torque teno virus 16-TUS01 | [AB017613] | (TTV16-TUS01) |
| Torque teno virus 17 |
|
|
| Torque teno virus 17-SENV-G | [AX025830] | (TTV17-SENV-G) |
| Torque teno virus 18 |
|
|
| Torque teno virus 18-SENV-C | [AX025718] | (TTV18-SENV-C) |
| Torque teno virus 19 |
|
|
| Torque teno virus 19-SANBAN | [AB025946] | (TTV19-SANBAN) |
| Torque teno virus 20 |
|
|
| Torque teno virus 20-SAa-10 | [AB060594] | (TTV20-SAa-10) |
| Torque teno virus 21 |
|
|
| Torque teno virus 21-TCHN-B | [AF348409] | (TTV21-TCHN-B) |
| Torque teno virus 22 |
|
|
| Torque teno virus 22-svi-1 | [AX174942] | (TTV22-svi-1) |
| Torque teno virus 23 |
|
|
| Torque teno virus 23-CH65-2 | [AB049607] | (TTV23-CH65-2) |
| Torque teno virus 24 |
|
|
| Torque teno virus 24-SAa-01 | [AB060597] | (TTV24-SAa-01) |
| Torque teno virus 25 |
|
|
| Torque teno virus 25-Mf-TTV9 | [AB041959] | (TTV25-Mf-TTV9) |
| Torque teno virus 26 |
|
|
| Torque teno virus 26-Mf-TTV3 | [AB041958] | (TTV26-Mf-TTV3) |
| Torque teno virus 27 |
|
|
| Torque teno virus 27-CT23F | [AB064595] | (TTV27-CT23F) |
| Torque teno virus 28 |
|
|
| Torque teno virus 28-CT43F | [AB064598] | (TTV28-CT43F) |
| Torque teno virus 29 |
|
|
| Torque teno virus 29-yonKC009 | [AB038621] | (TTV29-yonKC009) |
Species names are in italic script; names of isolates are in roman script. Sequence accession numbers [ ] and assigned abbreviations ( ) are also listed.
List of other related viruses which may be members of the genus Alphatorquevirus but have not been approved as species
None reported.
Genus Betatorquevirus
Type species Torque teno mini virus 1
Distinguishing features
The genus contains viruses identified in humans and non-human primates, with genomes ranging from about 2.8 to 2.9 kb.
Species demarcation criteria in the genus
Based on analysis of ORF1 in its entirety, a cut-off value of 35% nucleotide sequence identity is applied as a demarcation criterion.
List of species in the genus Betatorquevirus
| Torque teno mini virus 1 |
|
|
| Torque teno mini virus 1-CBD279 | [AB026931] | (TTMV1-CBD279) |
| Torque teno mini virus 2 |
|
|
| Torque teno mini virus 2-NLC023 | [AB038629] | (TTMV2-NLC023) |
| Torque teno mini virus 3 |
|
|
| Torque teno mini virus 3-NLC026 | [AB038630] | (TTMV3-NLC026) |
| Torque teno mini virus 4 |
|
|
| Torque teno mini virus 4-Pt-TTV8-II | [AB041963] | (TTMV4-Pt-TTV8-II) |
| Torque teno mini virus 5 |
|
|
| Torque teno mini virus 5-TGP96 | [AB041962] | (TTMV5-TGP96) |
| Torque teno mini virus 6 |
|
|
| Torque teno mini virus 6-CBD203 | [AB026929] | (TTMV6-CBD203) |
| Torque teno mini virus 7 |
|
|
| Torque teno mini virus 7-CLC156 | [AB038627] | (TTMV7-CLC156) |
| Torque teno mini virus 8 |
|
|
| Torque teno mini virus 8-PB4TL | [AF291073] | (TTMV8-PB4TL) |
| Torque teno mini virus 9 |
|
|
| Torque teno mini virus 9-NLC030 | [AB038631] | (TTMV9-NLC030) |
Species names are in italic script; names of isolates are in roman script. Sequence accession numbers [ ] and assigned abbreviations ( ) are also listed.
List of other related viruses which may be members of the genus Betatorquevirus but have not been approved as species
| Torque teno mini virus-LIL-y1 | [EF538880] | (TTMV-LIL-y1) |
| Torque teno mini virus-LIL-y2 | [EF538881] | (TTMV-LIL-y2) |
| Torque teno mini virus-LIL-y3 | [EF538882] | (TTMV-LIL-y3) |
Genus Gammatorquevirus
Type species Torque teno midi virus 1
Distinguishing features
The genus contains viruses identified in humans and non-human primates, with genomes of about about 3.2 kb. Some isolates harbouring shorter genomes (ca. 2–2.6 kb) have been identified.
Species demarcation criteria in the genus
Based on analysis of ORF1 in its entirety, a cut-off value of 35% nucleotide sequence identity is applied as a demarcation criterion.
List of species in the genus Gammatorquevirus
| Torque teno midi virus 1 |
|
|
| Torque teno midi virus 1-MD1-073 | [AB290918] | (TTMDV1-MD1-073) |
| Torque teno midi virus 2 |
|
|
| Torque teno midi virus 2-MD2-013 | [AB290919] | (TTMDV2-MD2-013) |
Species names are in italic script; names of isolates are in roman script. Sequence accession numbers [ ] and assigned abbreviations ( ) are also listed.
List of other related viruses which may be members of the genus Gammatorquevirus but have not been approved as species
| Torque teno midi virus-2PoSMA | [EF538875] | (TTMDV-2PoSMA) |
| Torque teno midi virus-6PoSMA | [EF538876] | (TTMDV-6PoSMA) |
| Torque teno midi virus-MDJHem2 | [AB303552] | (TTMDV-MDJHem2) |
| Torque teno midi virus-MDJHem3-1 | [AB303553] | (TTMDV-MDJHem3-1) |
| Torque teno midi virus-MDJHem3-2 | [AB303554] | (TTMDV-MDJHem3-2) |
| Torque teno midi virus-MDJHem5 | [AB303555] | (TTMDV-MDJHem5) |
| Torque teno midi virus-MDJN2 | [AB303559] | (TTMDV-MDJN2) |
| Torque teno midi virus-MDJN14 | [AB303560] | (TTMDV-MDJN14) |
| Torque teno midi virus-MDJN47 | [AB303561] | (TTMDV-MDJN47) |
| Torque teno midi virus-MDJN51 | [AB303562] | (TTMDV-MDJN51) |
| Torque teno midi virus-MDJN69 | [AB303564] | (TTMDV-MDJN69) |
| Torque teno midi virus-MDJN97 | [AB303566] | (TTMDV-MDJN97) |
| Torque teno midi virus-Pt-TTMDV210 | [AB449062] | (TTMDV-Pt-TTMDV210) |
Genus Deltatorquevirus
Type species Torque teno tupaia virus
Distinguishing features
The genus contains virus identified in tupaia.
Species demarcation criteria in the genus
Not applicable.
List of species in the genus Deltatorquevirus
| Torque teno tupaia virus |
|
|
| Torque teno tupaia virus-Tbc-TTV14 | [AB057358] | (TTTuV-Tbc-TTV14) |
Species names are in italic script; names of isolates are in roman script. Sequence accession numbers [ ] and assigned abbreviations ( ) are also listed.
List of other related viruses which may be members of the genus Deltatorquevirus but have not been approved as species
None reported.
Genus Epsilontorquevirus
Type species Torque teno tamarin virus
Distinguishing features
The genus contains a virus identified in the cotton-top tamarin.
Species demarcation criteria in the genus
Not applicable.
List of species in the genus Epsilontorquevirus
| Torque teno tamarin virus |
|
|
| Torque teno tamarin virus-So-TTV2 | [AB041960] | (TTTaV-So-TTV2) |
Species names are in italic script; names of isolates are in roman script. Sequence accession numbers [ ] and assigned abbreviations ( ) are also listed.
List of other related viruses which may be members of the genus Epsilontorquevirus but have not been approved as species
None reported.
Genus Zetatorquevirus
Type species Torque teno douroucouli virus
Distinguishing features
The genus contains virus identified in the douroucouli (owl monkey or night monkey).
Species demarcation criteria in the genus
Not applicable.
List of species in the genus Zetatorquevirus
| Torque teno douroucouli virus |
|
|
| Torque teno douroucouli virus-At-TTV3 | [AB041961] | (TTDoV-At-TTV3) |
Species names are in italic script; names of isolates are in roman script. Sequence accession numbers [ ] and assigned abbreviations ( ) are also listed.
List of other related viruses which may be members of the genus Zetatorquevirus but have not been approved as species
None reported.
Genus Etatorquevirus
Type species Torque teno felis virus
Distinguishing features
The genus contains viruses identified in the domestic cat.
Species demarcation criteria in the genus
Not applicable.
List of species in the genus Etatorquevirus
| Torque teno felis virus |
|
|
| Torque teno felis virus-Fc-TTV4 | [AB076003] | (TTFeV-Fc-TTV4) |
Species names are in italic script; names of isolates are in roman script. Sequence accession numbers [ ] and assigned abbreviations ( ) are also listed.
List of other related viruses which may be members of the genus Etatorquevirus but have not been approved as species
| Torque teno felis virus-PRA1 | [EF538877] | (TTFeV-Fc-PRA1) |
Genus Thetatorquevirus
Type species Torque teno canis virus
Distinguishing features
The genus contains virus identified in the domestic dog.
List of species demarcation criteria in the genus
Not applicable.
List of species in the genus Thetatorquevirus
| Torque teno canis virus |
|
|
| Torque teno canis virus-Cf-TTV10 | [AB076002] | (TTCaV-Cf-TTV10) |
Species names are in italic script; names of isolates are in roman script. Sequence accession numbers [ ] and assigned abbreviations ( ) are also listed.
List of other related viruses which may be members of the genus Thetatorquevirus but have not been approved as species
None reported.
Genus Iotatorquevirus
Type species Torque teno sus virus 1
Distinguishing features
The genus contains viruses identified in the pig.
Species demarcation criteria in the genus
Based on analysis of ORF1 in its entirety, a cut-off value of 35% nucleotide sequence identity is applied as a demarcation criterion.
List of species in the genus Iotatorquevirus
| Torque teno sus virus 1 |
|
|
| Torque teno sus virus 1-Sd-TTV31 | [AB076001] | (TTSuV1-Sd-TTV31) |
| Torque teno sus virus 2 |
|
|
| Torque teno sus virus 2-1p | [AY823990] | (TTSuV2-1p) |
Species names are in italic script; names of isolates are in roman script. Sequence accession numbers [ ] and assigned abbreviations ( ) are also listed.
List of other related viruses which may be members of the genus Iotatorquevirus but have not been approved as species
| Torque teno sus virus-2p | [AY823991] | (TTSuV-2p) |
Note: The nucleotide sequence of this virus identified in swine presents a degree of sequence divergence compatible with the creation of a distinct genus. However, it has been proposed to classify this virus in the genus Iotatoquevirus until further data have been collected in swine species.
List of other related viruses which may be members of the family Anelloviridae but have not been approved as species
| Torque teno zalophus virus – ZcAV | [FJ459582] | (TTZaV-ZcAV) |
Note: virus identified in California sea lion.
Phylogenetic relationships within the family
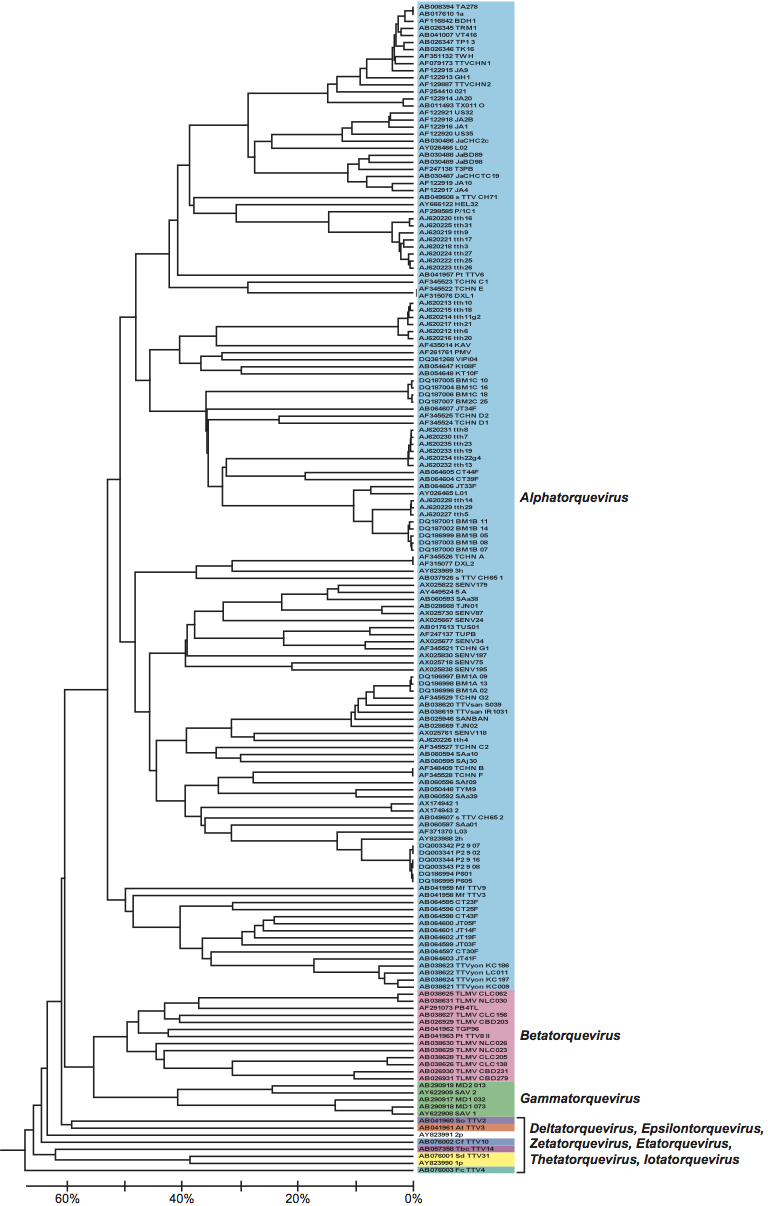
The progressive discovery of highly divergent, complete genomes ranging from about 2 to 4 kb in humans and other animals impairs a reliable phylogenetic and taxonomic analysis of full-length sequences. Based on these considerations, the analysis of the entire ORF1 at the nucleotide level (ORF1-nt) is the most convenient approach. Analysis of the distribution of pairwise comparisons and the corresponding phylogenetic tree (see Figure 3) facilitates identification of the levels of genera and species. Based on the currently available data, a taxonomic classification is proposed with the following cut-off values for sequence divergence: genera >56%, species >35%.
Similarity with other taxa
Members of the family Anelloviridae have features in common with Chicken anaemia virus, the type species of genus Gyrovirus, family Circoviridae. Namely:
- All viruses possess negative sense, circular, ssDNA genomes.
- The genome organizations are similar.
- The CP of CAV and the putative CPs of anelloviruses both possess amino acid sequence motifs that are characteristic of RCR Rep proteins. The proteins encoded by ORF2 in CAV, TTVs and TTMVs contain amino acid sequences that are characteristic of protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPase). ORF2 in anelloviruses and CAV share a common motif, WX7HX3CXCX5H.
- The non-coding region of the CAV genome and those of most anellovirus genomes contain G+C-rich sequences.
- Spliced transcripts have been detected for CAV and TTV.
- Peptides identified in CAV and TTV are able to induce apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines.
Derivation of names
Anello: from Latin anello, “ring”.
Torque: from Latin torques, “necklace”.
Teno: from Latin tenuis, “thin”.
Mini: from Latin minimus, “small”.
Midi: from Latin medius, “intermediate”.
Further reading
Biagini, P. (2009). Classification of TTV and related viruses (anelloviruses). Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol., 331, 21-33.
Biagini, P., Uch, R., Belhouchet, M., Attoui, H., Cantaloube, J.F., Brisbarre, N. and de Micco, P. (2007). Circular genomes related to anelloviruses identified in human and animal samples using a combined rolling-circle amplification- sequence independent single primer amplification approach. J. Gen. Virol., 88, 2696-2701.
Jelcic, I., Hotz-Wagenblatt, A., Hunziker, A., Zur Hausen, H. and de Villiers, E.M. (2004). Isolation of multiple TT virus genotypes from spleen biopsy tissue from a Hodgkin's disease patient: genome reorganization and diversity in the hypervariable region. J. Virol., 78, 7498-7507.
Jones, M.S., Kapoor, A., Lukashov, V.V., Simmonds, P., Hecht, F. and Delwart, E. (2005). New DNA viruses identified in patients with acute viral infection syndrome. J. Virol., 79, 8230-8236.
Niel, C., Diniz-Mendez, L. and Devalle, S. (2005). Rolling-circle amplification of Torque teno virus (TTV) complete genomes from human and swine sera and identification of a novel swine TTV genogroup. J. Gen. Virol., 86, 1343-1347.
Ninomiya, M., Nishizawa T., Takahashi, M., Lorenzo, F.R., Shimosegawa, T. and Okamoto, H. (2007). Identification and genomic characterization of a novel human torque teno virus of 3.2 kb. J. Gen. Virol., 88, 1939-1944.
Nishizawa, T., Okamoto, H., Konishi, K., Yoshizawa, H., Miyakawa, Y. and Mayumi, M. (1997). A novel DNA virus (TTV) associated with elevated transaminase levels in posttransfusion hepatitis of unknown etiology. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 241, 92-97.
Okamoto, H. (2009). TT viruses in animals. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol., 331, 1-20.
Peng, Y.H., Nishizawa, T., Takahashi, M., Ishikawa, T., Yoshikawa, A. and Okamoto, H. (2002). Analysis of the entire genomes of thirteen TT virus variants classifiable into the fourth and fifth genetic groups, isolated from viremic infants. Arch. Virol., 147, 21-41.
Takahashi, K., Iwasa, Y., Hijikata, M. and Mishiro, S. (2000). Identification of a new human DNA virus (TTV-like mini virus, TLMV) intermediately related to TT virus and chicken anemia virus. Arch. Virol., 145, 979-993.
Contributed by
Biagini, P., Bendinelli, M., Hino, S., Kakkola, L., Mankertz, A., Niel, C., Okamoto, H., Raidal, S., Teo, C.G. and Todd, D.
Figures
Figure 1 Negative contrast electron microscopy of particles of an isolate of Torque teno virus, stained with uranyl acetate. The bar represents 100 nm.
(From Itoh et al. (2000.) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 279, 718724.)

Figure 2 Genome organization of an isolate of Torque teno virus.
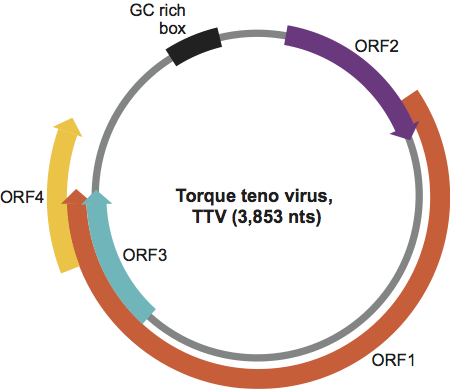
Figure 3 (opposite) UPGMA phylogenetic tree built for members of the family Anelloviridae, using ORF1-nt sequences (virus strains are identified on the figure by their GenBank accession numbers).