Family: Alphatetraviridae (Interim Report)
This is a summary page created by the ICTV Report Editors using information from associated Taxonomic Proposals and the Master Species List.
Edited by: Jens H. Kuhn
Posted: November 2024
Summary
The family Alphatetraviridae includes ssRNA(+) viruses of invertebrates (Table 1 Alphatetraviridae). The family Alphatetraviridae was established in 1981 (Master Species List #07); the family was originally named Nudaurelia beta virus group, and subsequently renamed (in 1987) Tetraviridae.
Table 1 Alphatetraviridae. Characteristics of members of the family Alphatetraviridae.
| Characteristic | Description |
| Example | Nudaurelia capensis beta virus (AF102884), species Betatetravirus nudaureliae, genus Betatetravirus |
| Virion | Icosahedral, 32–40 nm diameter, T=4 quasi-symmetry (Figure 1 Alphatetraviridae) |
| Genome | ssRNA(+), 1–2 linear segments, 6.6–8.0 kb with a 3′-terminal tRNA-like structure (Figure 2 Alphatetraviridae) |
| Replication | Cytoplasmic, in association with host cell membranes, through dsRNA intermediates |
| Translation | From genomic size and subgenomic size mRNAs, possibly involving read-through translation |
| Host range | Invertebrates (Lepidoptera) |
| Taxonomy | Realm Riboviria, kingdom Orthornavirae, phylum Kitrinoviricota, class Alsuviricetes, order Hepelivirales: 2 genera, 10 species (Figure 3 Alphatetraviridae) |
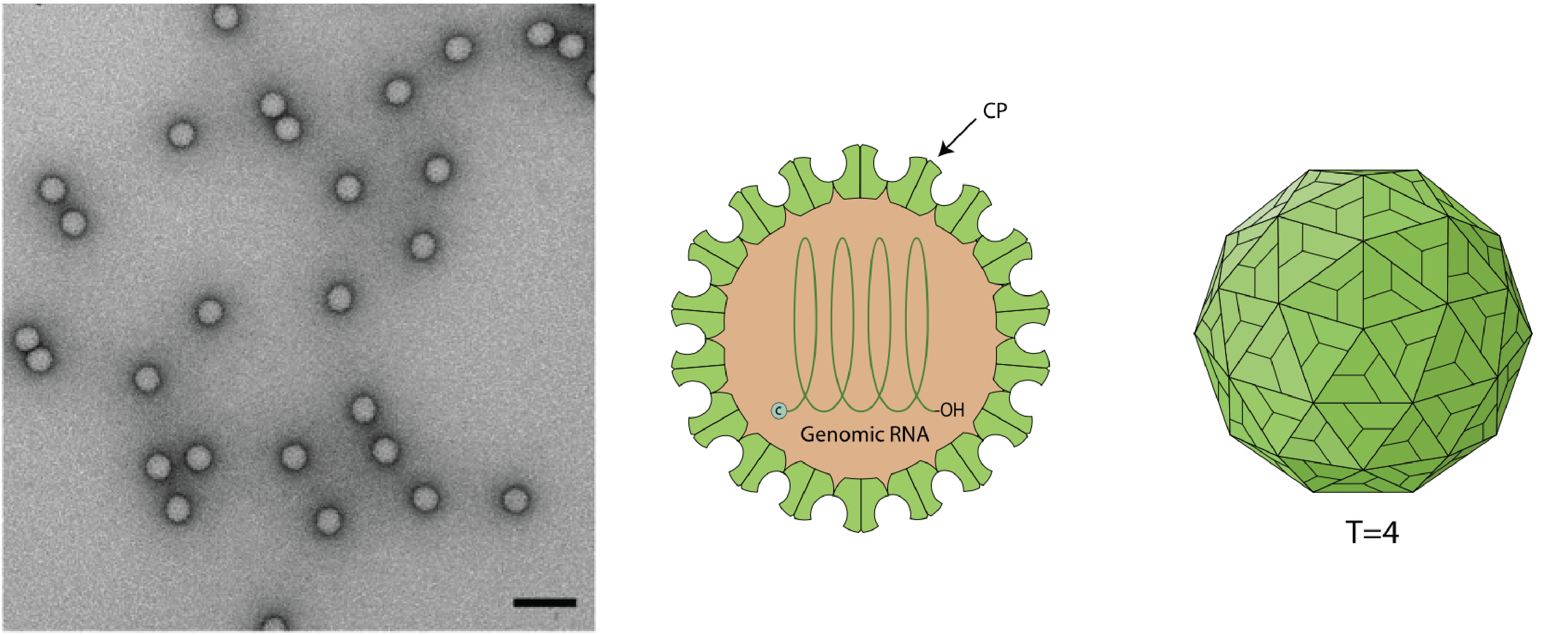 |
| Figure 1 Alphatetraviridae. (Left) Electron micrograph of purified Nudaurelia capensis omega virus capsid protein expressed in Nicotiana benthamiana and negatively-stained with 2% (w/v) uranyl acetate. Scale bar = 100 nm. The image is Figure 1 from Castells-Graells R, Ribeiro JRS, Domitrovic T, Hesketh EL, Scarff CA. et al. Plant-expressed virus-like particles reveal the intricate maturation process of a eukaryotic virus. Commun Biol. 2021 4:619 under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (Right) Schematic of virion (image from ViralZone (viralzone.expasy.org, used under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, credit: SwissBioPics) |
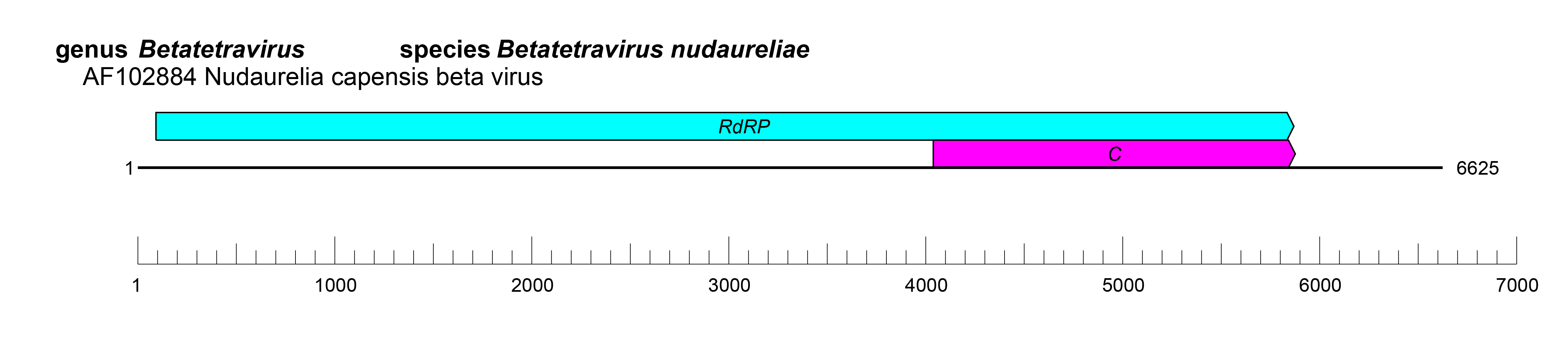 |
| Figure 2 Alphatetraviridae. Genome organisation of Nudaurelia capensis beta virus, a member of the family Alphatetraviridae. Boxes indicate open reading frames as annotated on GenBank accession AF102884. RdRP, RNA-directed RNA polymerase; C, coat protein. |
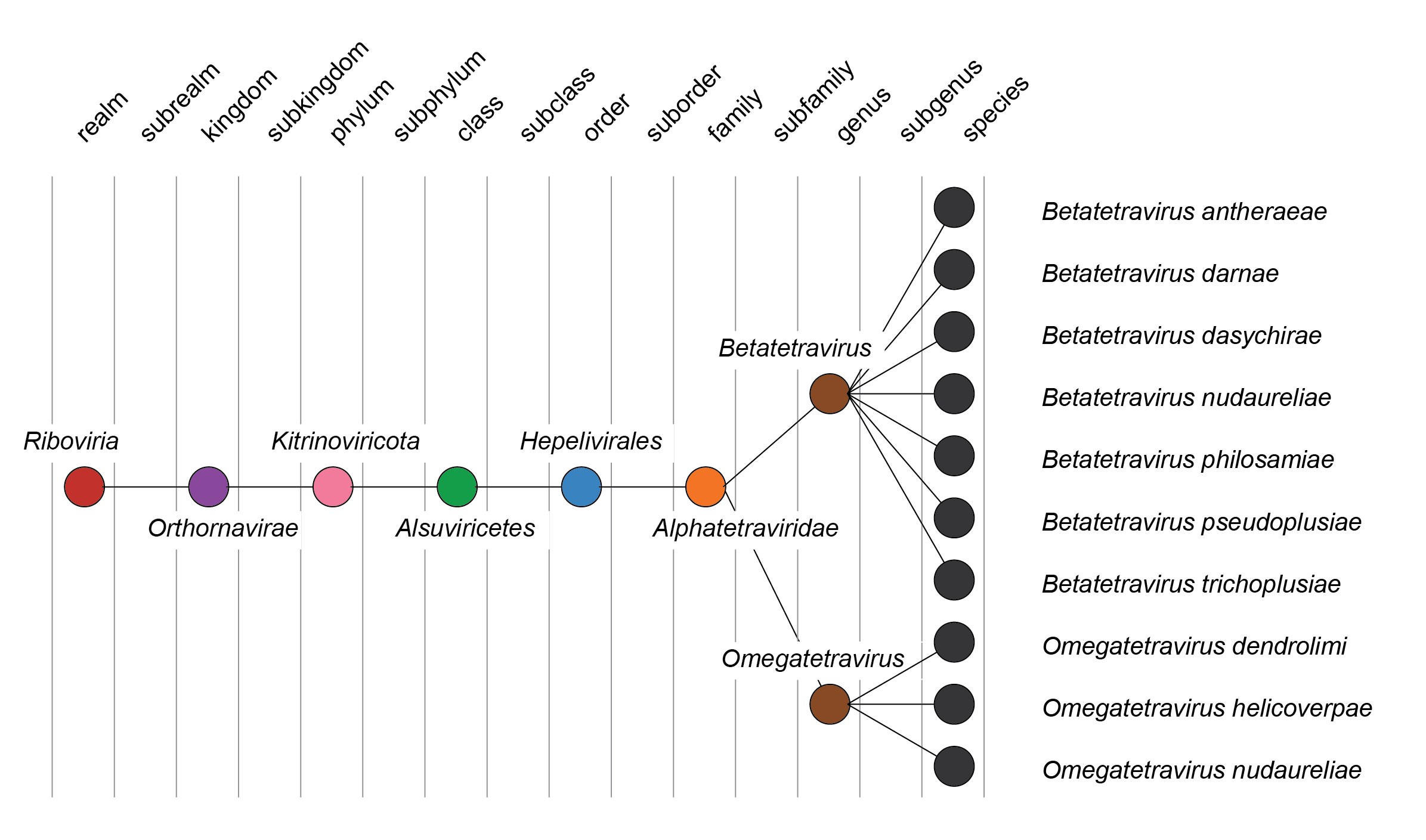 |
| Figure 3 Alphatetraviridae. Taxonomy of the family Alphatetraviridae. |
Derivation of names
Alphatetraviridae: from the Ancient Greek ἄλφα (álpha), the first letter of the Greek alphabet and τετρα (tetra), the Greek cardinal 4, referring to the relationship to viruses of the Alpha-like supergroup in the replicase region and the T=4 capsid architecture that define the family; the suffix -viridae for family taxa
Betatetravirus: from the Ancient Greek βῆτα (bêta), the second letter of the Greek alphabet, referring to Nudaurelia capensis beta virus, a member of a species in the genus, and the defunct family name Tetraviridae
Omegatetravirus: from the Ancient Greek ωμέγα (omega), the twenty-fourth letter of the Greek alphabet, referring to Nudaurelia capensis omega virus, a member of a species in the genus, and the defunct family name Tetraviridae

