Family: Amalgaviridae (Interim Report)
This is a summary page created by the ICTV Report Editors using information from associated Taxonomic Proposals and the Master Species List.
Edited by: Luisa Rubino
Posted: October 2024
Summary
The family Amalgaviridae includes dsRNA viruses of plants (Table 1 Amalgaviridae). The virus genomes are monopartite and have two partially overlapping open reading frames that encode the RNA-directed RNA polymerase (RdRP) and a protein of unknown function. The family Amalgaviridae was established in 2014 (Master Species List #28).
Table 1 Amalgaviridae. Characteristics of members of the family Amalgaviridae.
| Characteristic | Description |
| Example | southern tomato virus (EF442780), species Amalgavirus lycopersici, genus Amalgavirus |
| Virion | Not known |
| Genome | dsRNA, monopartite, approx. 3.5 kbp (Figure 1 Amalgaviridae) |
| Replication | Not known |
| Translation | Involves +1 ribosomal frameshifting |
| Host range | Plants, asymptomatic, seed transmitted |
| Taxonomy | Realm Riboviria, kingdom Orthornavirae, phylum Pisuviricota, class Duplopiviricetes, order Durnavirales: 3 genera and 23 species (Figure 2 Amalgaviridae) |
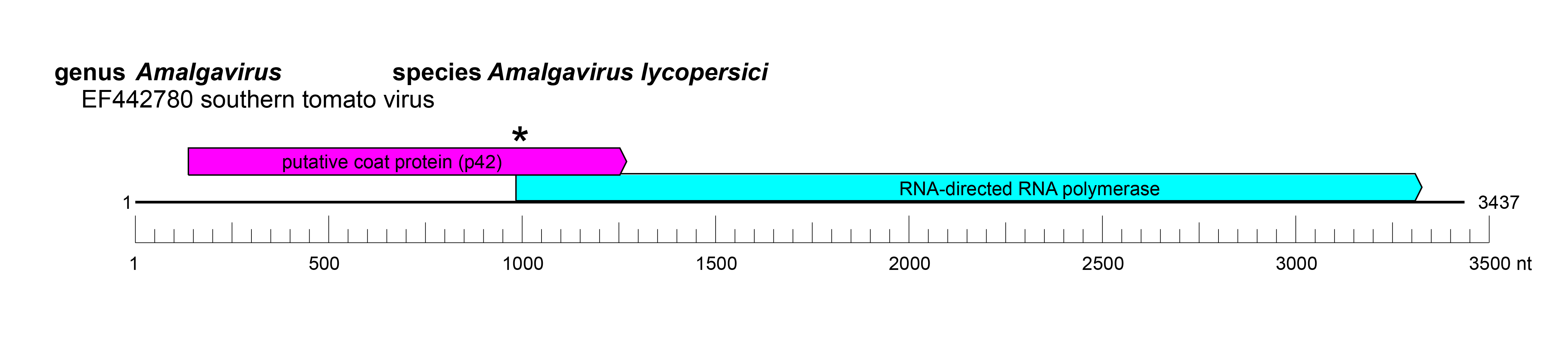 |
| Figure 1 Amalgaviridae. Genome organisation of southern tomato virus, a member of the family Amalgaviridae. Boxes indicate open reading frames as annotated on GenBank accession EF442780. * indicates a ribosomal slippage site. |
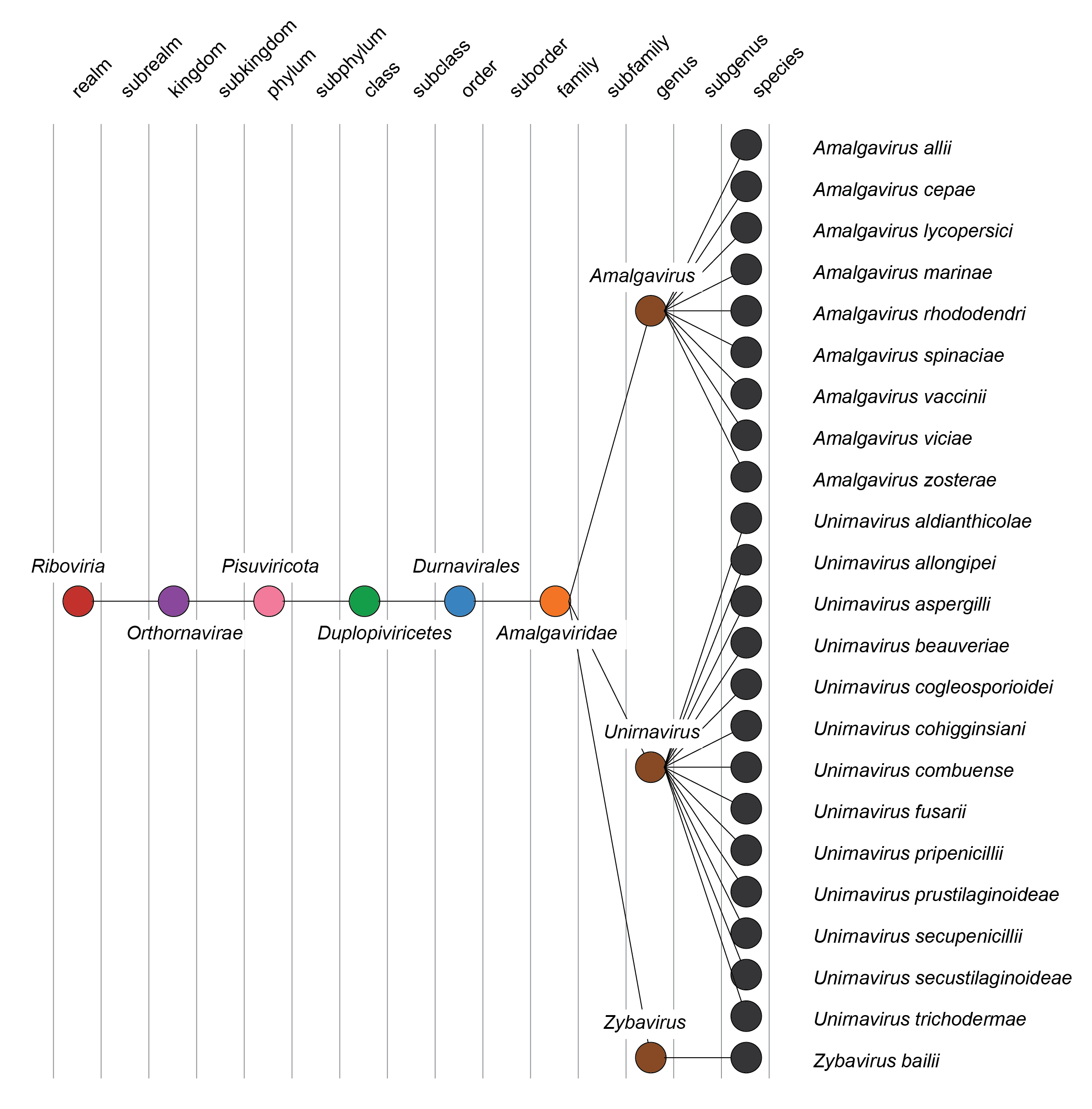 |
| Figure 2 Amalgaviridae. Taxonomy of the family Amalgaviridae. |
Derivation of names
Amalgaviridae, Amalgavirus: from the Medieval Latin amalgama, meaning "mercury alloy", referring to the fact that viruses of the family blend (or alloy) the properties of the viruses in the Partitiviridae (re: phylogeny) and Totiviridae (re: genome organization); the suffix -viridae for family taxa
Unirnavirus: from the Latin unicus, meaning ‘one’ or ‘single’, to indicate a non-segmented genome, and RNA
Zybavirus: from the initial two letters of the host, Zygosaccharomyces bailii: the suffix -virus for genus taxa

