Family: Halomagnusviridae (interim Report)
This is a summary page created by the ICTV Report Editors using information from associated Taxonomic Proposals and the Master Species List.
Edited by: Mart Krupovic
Posted: April 2023, updated December 2024
Summary
The family Halomagnusviridae includes double-stranded DNA viruses with icosahedral capsids and contractile helical tails, infecting hyperhalophilic archaea of the class Halobacteria (Table 1 Halmagnusviridae). The family was assigned to the realm Duplodnaviria and included in the class Caudoviricetes in 2022 (Master Species List 37).
Table 1 Halomagnusviridae. Characteristics of members of the family Halomagnusviridae.
| Characteristic | Description |
| Example | Halogranum tailed virus 1 (KC292026), species Hagravirus capitaneum, genus Hagravirus |
| Virion | Icosahedral capsid with a contractile helical tail (myoviral morphology) |
| Genome | Linear, double-stranded DNA genome of 144 kbp (Figure 1 Halomagnusviridae) |
| Replication | Lytic |
| Translation | Prokaryotic translation using viral mRNA and host ribosomes. Halogranum tailed virus 1 encodes 36 tRNAs for all universal genetic code amino acids |
| Host range | Halophilic members of the Archaea. Replicates in Halogranum sp. SS5-1 |
| Taxonomy | Realm Duplodnaviria, kingdom Heunggongvirae, phylum Uroviricota, class Caudoviricetes, order Thumleimavirales: 1 genus and 1 species (Figure 2 Halomagnusviridae) |
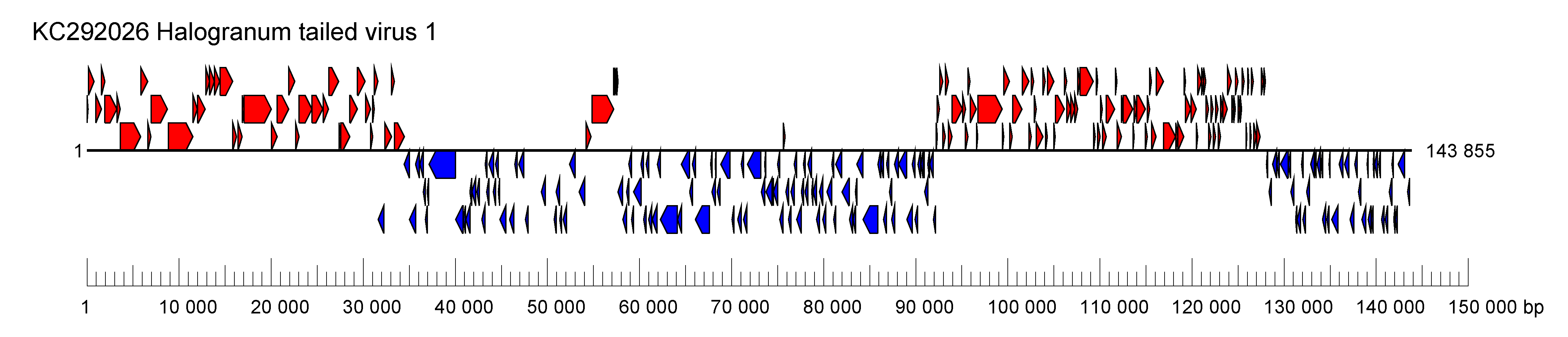 |
| Figure 1 Halomagnusviridae. Genome organisation of a member of the family Halomagnusviridae. Boxes indicate open reading frames as annotated on GenBank accession KC292026. |
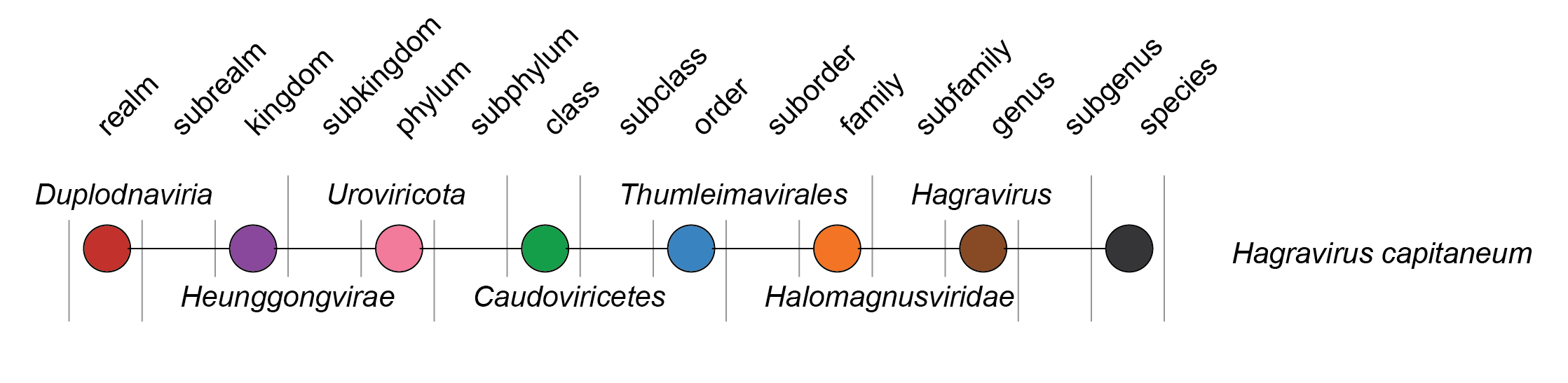 |
| Figure 2 Halomagnusviridae. Taxonomy of the family Halomagnusviridae. |
Derivation of name
Halomagnusviridae: from halophilic and magnus, the Latin word for large, referring to the fact that Halogranum tailed virus 1 has by far the largest genome among known haloarchaeal viruses.

