Family: Leishbuviridae
Scott Adkins, Katherine Brown, Juan Carlos de la Torre, Michele Digiaro, Holly R. Hughes, Sandra Junglen, Amy J. Lambert, Piet Maes, Marco Marklewitz, Gustavo Palacios, Takahide Sasaya (笹谷孝英), Massimo Turina, Yong-Zhen Zhang (张永振), and Jens H. Kuhn
*The citation for this ICTV Report chapter is the summary published as:
Corresponding author: Jens H. Kuhn ([email protected])
Edited by: Jens H. Kuhn and Stuart G. Siddell
Posted: November 2023, updated June 2024
Summary
Leishbuviridae is a family of negative-sense RNA viruses with genomes of about 8.0 kb (Table 1 Leishbuviridae). These viruses have been found in protists. The family includes a single genus with eleven species. The leishbuvirid genome consists of three monocistronic RNA segments with open reading frames (ORFs) that encode a nucleoprotein (NP), a glycoprotein (GP), and a large (L) protein containing an RNA-directed RNA polymerase (RdRP) domain.
Table 1 Leishbuviridae. Characteristics of members of the family Leishbuviridae
| Characteristic | Description |
| Example | Leptomonas moramango virus (S: KX280014; M: KX280013; L: KX280012), species Shilevirus leptomonadis |
| Virion | Unknown |
| Genome | About 8.0 kb of tri-segmented negative-sense RNA |
| Replication | Unknown |
| Translation | Unknown |
| Host range | Kinetoplastean protists |
| Taxonomy | Realm Riboviria, kingdom Orthornavirae, phylum Negarnaviricota, class Bunyaviricetes, order Hareavirales; the family includes one genus and eleven species |
Virion
Morphology
Unknown
Nucleic acid
Leishbuvirids have three RNA segments (small [S], medium [M], and large [L]) of linear negative-sense RNA with a total length of about 8.0 kb (S segment: 0.7–0.8 kb; M segment: about 1.2 kb; and L segment: about 6.0 kb) (Akopyants et al., 2016, Grybchuk et al., 2018a).
Genome organization and replication
Viruses of the family Leishbuviridae have a tri-segmented genome with three ORFs that encode an NP, a GP, and an L protein containing an RdRP domain (Akopyants et al., 2016) (Figure 1 Leishbuviridae).
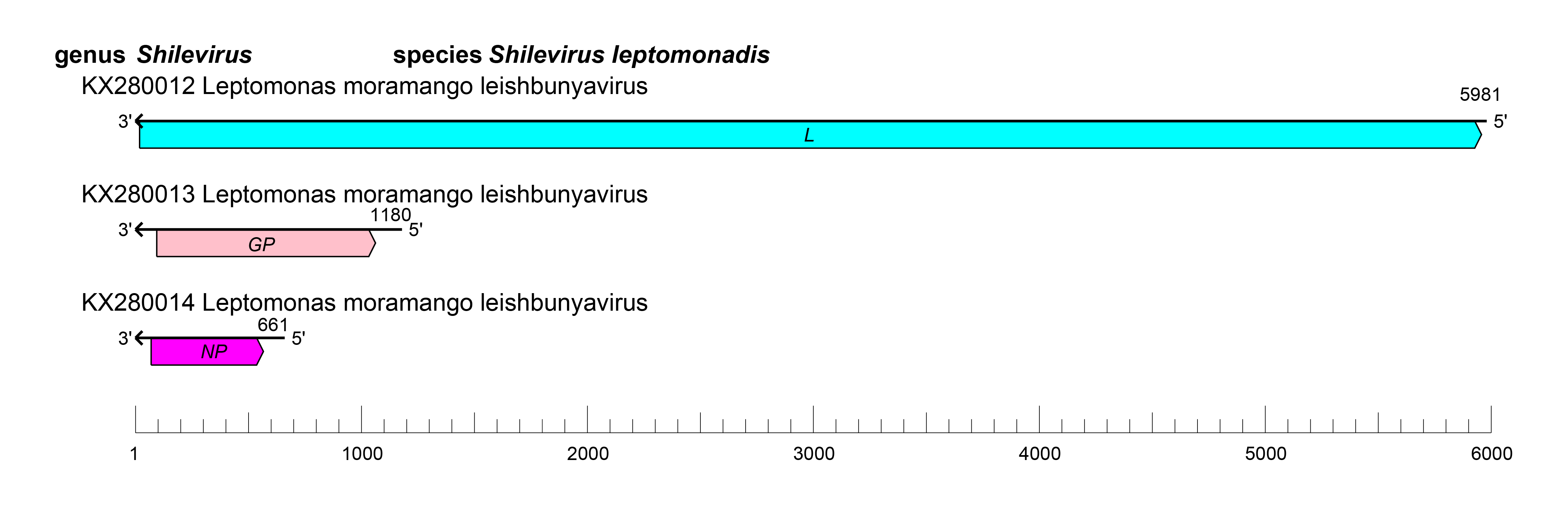 |
| Figure 1 Leishbuviridae. Genome organization of Leptomonas moramango virus. ORFs are colored according to the predicted protein function (GP, glycoprotein gene; L, large protein gene; NP, nucleoprotein gene). |
Biology
Leptomonas moramango virus (LEPMV), was detected in kinetoplastean protists (trypanosomatid Leptomonas moramango Yurchenko et al., 2014) in Madagascar (Akopyants et al., 2016).
Other leishbuvirids have been detected in (protists of) dipteran insects, such as culicid mosquitoes (Culex quinquefasciatus Say, 1823 in Zambia [unpublished, L: LC772153; L: LC772154; L: LC772155; L: OL700099; L: OL700101; L: OL700102; L: OL700112] and Ochlerotatus communis (de Geer, 1776) in Sweden (Ortiz-Baez et al., 2022)), unspecified phorid and tephritid fruit flies (Bactrocera correcta (Bezzi, 1916)) in China (Li et al., 2015, Grybchuk et al., 2018a, Zhang et al., 2022), ephydrid shore flies in China (Hydrellia griseola (Fallén, 1913)) (unpublished, L: MZ209735), and sarcophagid flesh flies in Australia (Mahar et al., 2020); in hymenopteran insects, such as bumblebees (apid Bombus spp.) (Klocek et al., 2023), honeybees (apid Apis mellifera Linnaeus, 1758) in South Africa and the USA (Remnant et al., 2017, Grybchuk et al., 2018a); in brown salor spiders (araneid Neoscona nautica (L. Koch, 1875)) in China (Li et al., 2015, Grybchuk et al., 2018a); in leeches in China (Shi et al., 2016, Grybchuk et al., 2018a); and directly in kinetoplastean protists (trypanosomatid Blechomonas sp, Crithidia sp., Leptomonas sp., and Phytomonas sp.) in the Czech Republic, Ecuador, and Madagascar (Akopyants et al., 2016, Grybchuk et al., 2018a, Grybchuk et al., 2018b, Grybchuk et al., 2020, Neri et al., 2022, Macedo et al., 2023, Mendes Junior et al., 2023).
Derivation of names
Leishbuviridae: a portmanteau of Leishmania and bunyavirus, referring to a genus of Trypanosomatidae, that includes the host of isolation of Leptomonas moramango virus , and the order Bunyavirales, which includes the virus family
leptomonadis: from the host genus Leptomonas
Shilevirus: scrambled from Leishmania
Genus demarcation criteria
Not applicable (the family includes only a single genus).
Relationships within the family
The genus includes eleven species.
Relationships with other taxa
Phylogenetic relationships of members of the family Leishbuviridae are shown in Figure 2 Leishbuviridae. Viruses in the family Leishbuviridae are most closely related to bunyaviral arenavirids, discoviridae, mypovirids, nairovirids, phenuivirids, and wupedevirids (Huang et al., 2019, Herath et al., 2020).
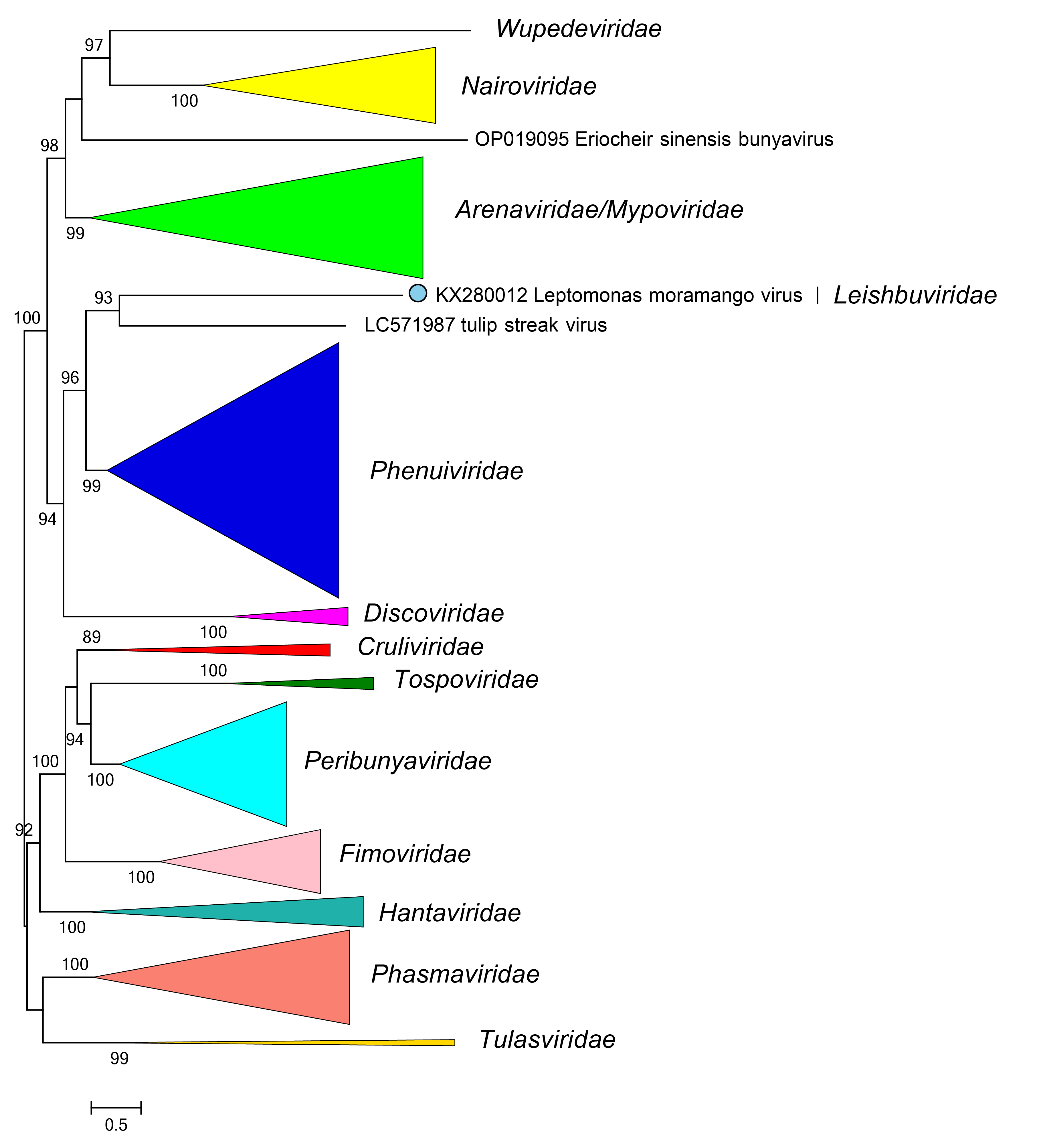 |
| Figure 2 Leishbuviridae. Phylogenetic relationships of Leptomonas moramango virus with other members of the class Bunyaviricetes. L protein sequences were aligned using MUSCLE and a maximum likelihood tree was produced using FastTree with default settings. Branches are collapsed for members of families apart from Leishbuviridae. Numbers at nodes indicated bootstrap support > 70%. |
Related, unclassified viruses
| Virus name | Accession number | Virus abbreviation | Reference |
| Apis bunyavirus 1 | L: KY354236 | (Remnant et al., 2017, Grybchuk et al., 2018a) | |
| Bactrocera correcta trypanosomatid leishbunyavirus | L: MW310338* | (Zhang et al., 2022) | |
| Blechmonas luni leishbunyavirus 1 | S: MG967336; M: MG967335; L: MG967334 | (Neri et al., 2022) | |
| Blechomonas ayalai leishbunyavirus 1 | S: MG967340; M: MG967339; L: MG967338 | (Grybchuk et al., 2018b) | |
| Blechomonas maslovi leishbunyavirus 1 | M: MG967343; L: MG967342 | (Neri et al., 2022) | |
| Boyle bunya-like virus | L: MT129682* | (Mahar et al., 2020) | |
| Crithidia abscondita leishbunyavirus | S: KX507299; M: KX507300; L: KX507301 | CabsLBV1 | (Grybchuk et al., 2018a) |
| Crithidia bombi leishbuvirus 1 | S: OR146998; M: OR146997; L: OR146996 | CbomLBV1 | (Klocek et al., 2023) |
| Crithidia otongatchiensis leishbunyavirus | S: KX451144; M: KX683300; L: KX451145 | CotoLBV1 | (Grybchuk et al., 2018a) |
| Crithidia pragensis leishbunyavirus 1 | L: KY322669* | CpraLBV1 | (Grybchuk et al., 2018a) |
| Crithidia sp. C4 leishbunyavirus 1 | L: KY322668* | CC4LBV1 | (Grybchuk et al., 2018a) |
| Crithidia sp. G15 leishbunyavirus 1 | L: KX373291 | CG15LBV1 | (Grybchuk et al., 2018a) |
| Crithidia sp. ZM leishbunyavirus 1 | L: KX373293 | CZMLBV1 | (Grybchuk et al., 2018a) |
| Culex leishbunyavirus 1 | L: LC772153 | ||
| Culex leishbunyavirus 2 | L: LC772154 | ||
| Culex leishbunyavirus 3 | L: LC772155 | ||
| Duke bunyavirus | S: KY094607; M: KY094606; L: KY094605 | DuBV | (Grybchuk et al., 2018a) |
| Gaddsjo leishbunyavirus | L: ON860448* | (Ortiz-Baez et al., 2022) | |
| Hángzhōu leishbuvirus | L: MZ209735* | HHFV | |
| Huángshí humpbacked fly virus | L: KM817669* | (Li et al., 2015, Grybchuk et al., 2018a) | |
| Húběi bunya-like virus 5 | L: KX884812* | HBLV5 | (Shi et al., 2016, Grybchuk et al., 2018a) |
| Húběi bunya-like virus 6 | L: KX884837* | HBLV6 | (Shi et al., 2016, Grybchuk et al., 2018a) |
| Leptomonas pyrrhocoris leishbunyavirus 1 | S: OP722871; L: OP722870 | LeppyrLBV1 | (Macedo et al., 2023) |
| Leptomonas pyrrhocoris leishbunyavirus 2 | S: OP722873; L: OP722872 | LeppyrLBV2 | (Macedo et al., 2023) |
| Leptomonas pyrrhocoris leishbunyavirus 3 | S: OP722879; M: OP722878; L: OP722877 | LeppyrLBV3 | (Macedo et al., 2023) |
| Leptomonas pyrrhocoris leishbunyavirus 4 | S: OP722876; M: OP722875; L: OP722874 | LeppyrLBV4 | (Macedo et al., 2023) |
| Leishmania martiniquensis leishbunyavirus 1 | S: MK356556; M: MK356555; L:MK356554 | LmarLBV1 | (Macedo et al., 2023) |
| Leptomonas moramango leishbunyavirus isolate LepmorLBV1b | S: KX280017; M: KX280016; L: KX280015 | LmorLBV1b | (Akopyants et al., 2016, Grybchuk et al., 2018a) |
| Phytomonas sp. TCC231 leishbunyavirus 1 | L: KY322667* | PTCCLBV1 | (Grybchuk et al., 2018a) |
| Wǔhàn spider virus | L: KM817699* | WSV | (Li et al., 2015, Grybchuk et al., 2018a) |
| Xiángyún bunya-arena-like virus 1 | L: OL700099 | ||
| Xiángyún bunya-arena-like virus 2 | L: OL700101 | ||
| Xiángyún bunya-arena-like virus 3 | L: OL700102 | ||
| Xiángyún bunya-arena-like virus 11 | L: OL700112 |
Virus names and virus abbreviations are not official ICTV designations.
* Incomplete genome

